Data Analytics for Business Professionals
in Analytics & VisualizationWhat you will learn?
Understand core analytics concepts, types, and their strategic business applications
Frame business problems systematically using structured frameworks like CRISP-DM and SMART methodology
Extract, manipulate, and prepare data from multiple sources using SQL and Excel
Perform statistical analysis, hypothesis testing, and descriptive analytics to validate business assumptions
Build predictive models to forecast business outcomes including demand, churn, and trends
Create compelling visualizations and data narratives that drive stakeholder engagement and decision-making
Apply analytics techniques to solve real business challenges in marketing, operations, finance, and customer management
Interpret machine learning applications and assess business viability of advanced analytical solutions
Develop operational and prescriptive analytics strategies for process optimization and resource allocation
About this course
Given the surge in AI and big data projects, business professionals must bridge the gap between technical teams and decision-makers. This course fosters a data-driven culture, enabling participants to translate analytics into actionable insights that drive innovation and business growth.
Recommended For
- Business leaders seeking data-driven insights
- Non-technical professionals upskilling in analytics
- Marketing and sales teams analyzing customer behavior
- Finance and operations professionals optimizing performance
- Consultants needing strong data interpretation skills
- Entrepreneurs using data for strategic decisions
Tags
Data Analytics for Business Professionals Course
Business Data Analytics Course
Data Analytics Course for Business Professionals
Business Analytics for Professionals Course
Data Analytics Course
Business Analytics Course
Data Analysis for Business
Data Analytics Training
Data Analytics Online Course
Data Analytics for Managers
Data Analytics for Executives
Data Analytics for Decision Making
Data Driven Decision Making Course
Analytics for Business Leaders
Business Intelligence and Analytics Course
Data Analytics for Beginners
Data Analytics for Non Technical Professionals
Basic Data Analytics Course
Introduction to Business Analytics
Business Analytics Fundamentals Course
Corporate Data Analytics Training
Data Analytics for Working Professionals
Business Analytics Professional Course
Data Analytics Upskilling Course
Data Analytics for Business Teams
Excel Data Analytics Course
Power BI for Business Analytics
Data Visualization for Business
KPI and Metrics Analysis Course
Descriptive Analytics for Business
Data Analytics Skills for Business
Learn Data Analytics for Business
Data Analytics for Business Growth
Practical Business Analytics Course
Comments (0)
Business analytics converts data into actionable insights that drive business success. Its evolution into a strategic discipline enables agile, evidence-based decisions. Business analysts play a vital role in bridging data and business needs.
Business analytics involves four key types: descriptive (understanding past events), diagnostic (explaining causes), predictive (forecasting the future), and prescriptive (recommending actions). Together, they empower organizations to make informed, proactive decisions and optimize business performance.
Analytics frameworks like CRISP-DM structure analytics projects for success, while business context analysis and the SMART framework ensure focused problem-solving. Defining impact metrics and engaging stakeholders are key to delivering actionable insights aligned with organizational goals.
A career in business analytics blends essential technical skills—including SQL, Python, and data visualization—with soft skills like communication and critical thinking. Awareness of industry trends and proactive professional development are vital for long-term success in emerging analytics roles.
Defining and identifying business problems starts with recognizing performance gaps and categorizing issues by impact area. Clarifying ambiguous problems, controlling scope, and using techniques like Five Whys help uncover root causes, enabling targeted and effective solutions.
Successful analytics projects consider organizational constraints, data quality, resource availability, and regulatory requirements. Aligning analytics efforts with these factors ensures practical, ethical, and impactful business solutions.
SMART objectives clarify analytics goals with specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound targets. Defining KPIs, setting realistic timelines, and creating accountability frameworks ensures analytics projects remain focused, trackable, and aligned to business success.
Successful stakeholder engagement involves identifying and prioritizing stakeholders, resolving conflicts constructively, and communicating analytics findings clearly. Employing structured frameworks ensures alignment and maximizes the impact of analytics-driven decisions.
Relational databases organize data into tables with clear structures, managed through SQL, a powerful language for querying and managing data. Popular RDBMS options like SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle support diverse business needs with different strengths.
SQL enables powerful data retrieval through selection, filtering, joining, and aggregation. Writing complex queries with subqueries and using aggregate functions allows business professionals to summarize and analyze data effectively for informed decision-making.
Effective data preparation and cleaning address quality issues, harmonize formats, handle missing and outlier data, and validate datasets. These practices ensure analytics are based on trustworthy data, enabling accurate and actionable business insights.
Organizing data into appropriate structures, creating calculated fields, normalizing values, and transforming raw inputs prepare data for effective analysis. These steps enable clearer insights, useful models, and reliable business intelligence.
Descriptive statistics summarize data using central tendency (mean, median, mode), dispersion (standard deviation, variance, range), and distribution shape (skewness, kurtosis). They enable clear data interpretation, pattern recognition, and informed business decision-making.
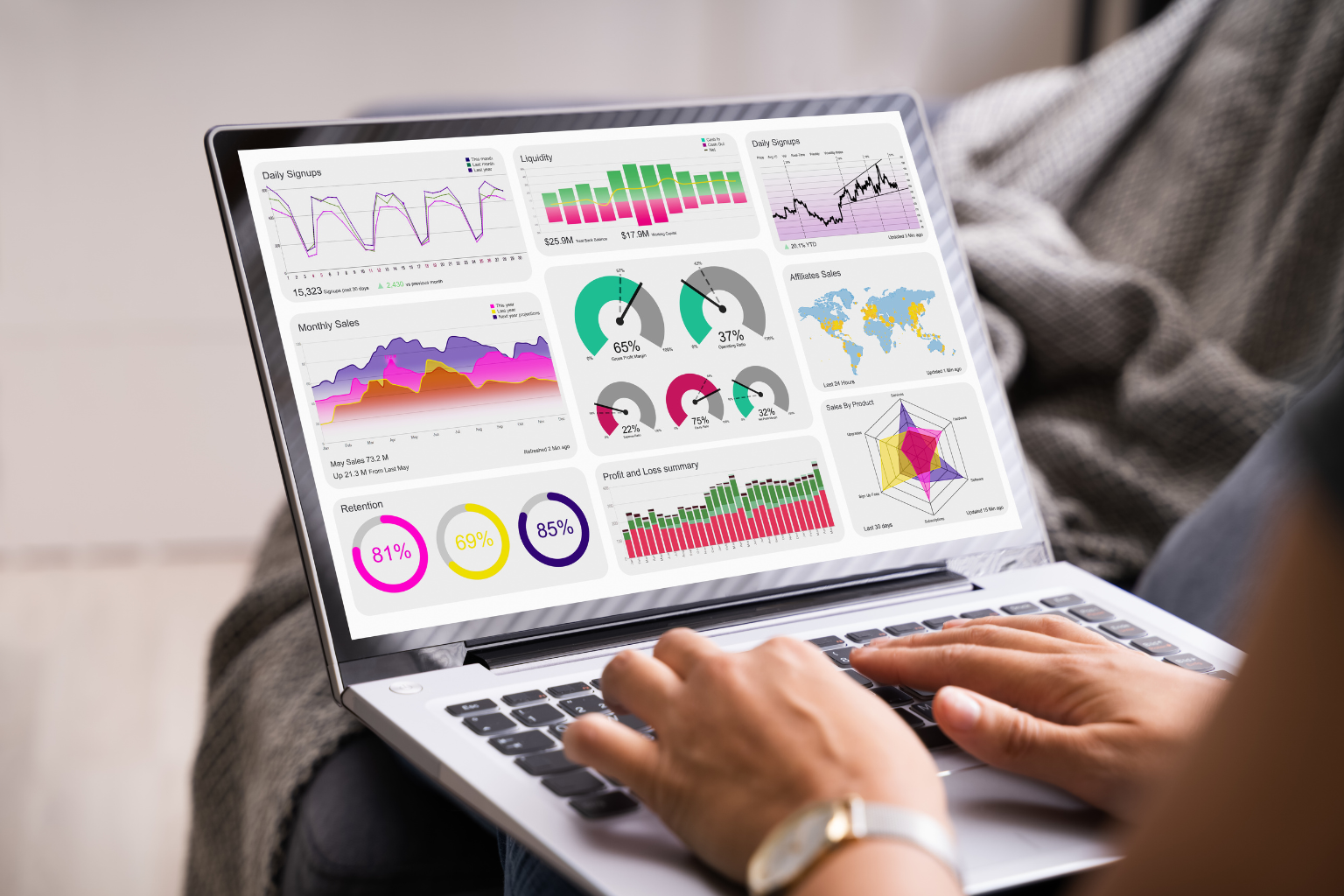
Effective data visualization employs appropriate chart types and visual techniques to reveal patterns and trends. Well-structured pivot tables and interactive dashboards enhance data exploration, enabling stakeholders to make informed, timely decisions.
Probability concepts, including distributions, sampling theory, confidence intervals, and margin of error, underpin informed business decisions. These tools quantify uncertainty and risk, enabling businesses to forecast outcomes and optimize strategies confidently.
Choosing appropriate sampling strategies, determining sample sizes, and applying suitable data collection methods ensure high-quality, representative data. Recognizing and mitigating sampling bias enhances the validity of business analytics and decision-making.
Hypothesis testing uses null and alternative hypotheses to statistically evaluate business claims while managing Type I and II errors. Selecting appropriate test directions and correctly interpreting p-values ensure reliable, data-driven decisions.
T-tests compare two group means, chi-square tests evaluate categorical relationships, ANOVA analyzes variance across multiple groups, and effect size measures real-world impact of findings. Together, these statistical tools empower businesses to make data-driven, impactful decisions.
Hypothesis testing underpins critical business applications including A/B marketing tests, quality assurance, process enhancement, and market research. These data-driven approaches empower companies to validate strategies, maintain standards, and optimize operations with confidence.
Confidence intervals provide a quantitative range for population parameters, aiding in reliable data interpretation. They support business decisions by clarifying estimate precision, informing resource allocation, and framing risk-based decision thresholds.
Excel’s advanced functions like VLOOKUP and INDEX-MATCH facilitate accurate data retrieval. SUMIF and COUNTIF enable conditional summarization. Conditional formatting and array formulas enhance visualization and complex analyses. Financial and statistical functions support critical business evaluations.
Pivot tables provide flexible, multi-dimensional data summaries. Grouping, calculated fields, slicers, and timelines enhance exploration and interactivity, empowering business users to generate detailed, actionable reports effortlessly.
Excel’s Data Model and Power Pivot empower users to analyze large, multi-source data by defining table relationships and applying advanced calculations. Combined with Power Query for efficient data preparation, these tools support complex financial reporting and sophisticated analytics within Excel.
Scenario analysis techniques like sensitivity analysis illuminate how variable changes affect outcomes. Excel's Solver optimizes decision variables under constraints, Goal Seek finds necessary inputs to achieve targets, and Scenario Manager compares multiple business alternatives, collectively enabling optimal, data-informed business strategies.
Effective data visualization leverages visual hierarchy and color theory to emphasize key insights while avoiding misleading elements and clutter. Incorporating accessibility principles ensures inclusivity, making data comprehensible and impactful for all audiences.
Data storytelling structures narratives around problems, insights, and actions, starting with clear conclusions and revealing details progressively. Connecting data to business and human outcomes makes stories compelling and actionable, fostering informed decision-making.
Tableau excels in interactive visual storytelling across diverse data sources, while Power BI offers seamless integration with Microsoft ecosystems. Both enable tailored dashboard designs and intuitive drill-down features, empowering users to explore data deeply and make informed decisions.
Tailoring visual communications to stakeholder needs, crafting concise, data-backed executive summaries, and building persuasive visual business cases are key to effective executive engagement. Presenting limitations transparently ensures trust and sound decision-making.
Customer analytics uses CLV calculations, cohort analysis, and customer journey mapping, supported by transactional, behavioral, and psychographic data. These methods unveil deep customer insights, guiding personalized, profit-driven business strategies.
Market segmentation strategies—demographic, behavioral, psychographic, and geodemographic—enable precise targeting by grouping customers with similar traits, behaviors, or lifestyles. These approaches help customize marketing, improve customer engagement, and increase business effectiveness.
Churn analysis uses predictive models to identify at-risk customers and understand churn drivers, enabling targeted retention strategies. Measuring initiative effectiveness ensures continuous improvement in reducing customer attrition and maximizing value.
Personalized marketing and recommendation systems tailored from diverse customer data boost engagement and sales. Operational analytics improves customer service efficiency, while privacy compliance safeguards customer trust, ensuring sustainable personalization strategies.
Operational analytics frameworks integrate defined KPIs, bottleneck identification, real-time dashboards, and continuous improvement to optimize business processes. This analytical approach enables efficient, data-backed operational management and agile responses to changing conditions.
Demand forecasting leverages historical patterns and sophisticated time series models to predict future demand, enabling optimized inventory management. Predictive analytics further reduce stockouts and excess stock through precise, data-driven decision-making.
Supply chain optimization integrates data for full visibility, streamlines logistics to reduce costs, improves supplier management through analytics, and strengthens risk resilience via contingency planning. These practices enhance efficiency, reduce expenses, and elevate the overall customer experience.
Monte Carlo simulation models uncertainties quantitatively, sensitivity analysis identifies key variables’ impacts, scenario modeling compares operational futures, and decision trees articulate complex decisions visually. Together, these techniques equip businesses to optimize operations and navigate uncertainty effectively.
Predictive modeling leverages supervised and unsupervised techniques within a structured lifecycle involving training, validation, and testing. Feature engineering enhances model relevance, while evaluation metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score guide effectiveness assessment, enabling precise business forecasts.
Regression analysis predicts business outcomes by modeling variable relationships. Linear and multiple regression estimate continuous outcomes, logistic regression forecasts binary events, and interpreting coefficients alongside significance tests ensures robust, actionable forecasts.
Time series forecasting analyzes trends, seasonality, and cycles in data to predict future outcomes. Methods like moving averages, exponential smoothing, and ARIMA models provide varied complexities. Evaluating model accuracy with metrics ensures reliable forecasting for effective business planning.
Predictive modeling transforms business operations by enabling accurate sales forecasts, early churn detection, preventive equipment maintenance, and agile market demand planning. These applications increase efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability through data-driven foresight.
Machine learning empowers predictive and descriptive analyses by learning from data via supervised (classification, regression) and unsupervised (clustering) methods. Its workflow includes problem framing, data preparation, and careful model selection, blending statistical foundations with computational techniques.
Decision trees offer transparent classification, random forests improve prediction robustness through ensemble learning, and Naive Bayes provides efficient probabilistic classifications. Model interpretability is essential for building trust and understanding in business decision contexts.
Machine learning applications such as fraud detection, customer segmentation, recommendation systems, and predictive maintenance enable organizations to optimize operations, personalize experiences, and proactively manage risks. These solutions drive efficiency and enhance competitiveness in today's data-driven economy.
Successful ML in business hinges on ethical AI practices, stringent data quality, a balance between model complexity and interpretability, and thorough cost-benefit analyses. Addressing these considerations enables organizations to deploy reliable, responsible, and impactful ML solutions.
Financial data analysis involves evaluating balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements alongside key ratios to assess a company's profitability, liquidity, and operational effectiveness. This comprehensive analysis supports informed decision-making, investment evaluation, and strategic planning.
Cost analysis distinguishes fixed and variable expenses, employs break-even analysis to identify profitability thresholds, forecasts future costs for planning, and uses variance analysis to explain budget deviations. These practices enable businesses to optimize costs and enhance financial performance.
Pricing analytics combines price elasticity insights, competitive analysis, dynamic strategies, and price-volume optimization to drive profitability. By integrating customer and market data, businesses execute responsive, informed pricing decisions that align with market realities and maximize revenue.
Investment and risk analysis employ capital budgeting to prioritize projects, scenario analysis for comprehensive financial planning, risk assessment to manage vulnerabilities, and ROI calculations to justify investments. Together, these tools enable informed, strategic, and financially sound decisions.
Defining project scope begins with selecting a feasible, impactful business problem, setting SMART objectives, establishing quantifiable success metrics, and precisely outlining data and resource requirements. This structured approach ensures aligned efforts and measurable outcomes.
The end-to-end analytics workflow encompasses business understanding, meticulous data handling, rigorous analysis, and effective communication of insights, ensuring data-driven decision-making aligns with organizational objectives.
Business recommendation development entails converting analytical insights into context-sensitive, actionable strategies with measurable impacts. A detailed implementation roadmap coupled with success metrics underpins effective execution and continuous improvement.
Professional presentation involves concise executive summaries, compelling visual storytelling, tailored communication to diverse audiences, and transparent handling of questions and limitations. Mastery of these elements ensures analytics drive informed, confident business decisions.