Deploying applications on AWS enables organizations to leverage scalable and reliable cloud infrastructure to deliver services efficiently to users.
Basic application deployment in AWS involves provisioning compute resources, configuring networking, deploying application code, and managing storage and security.
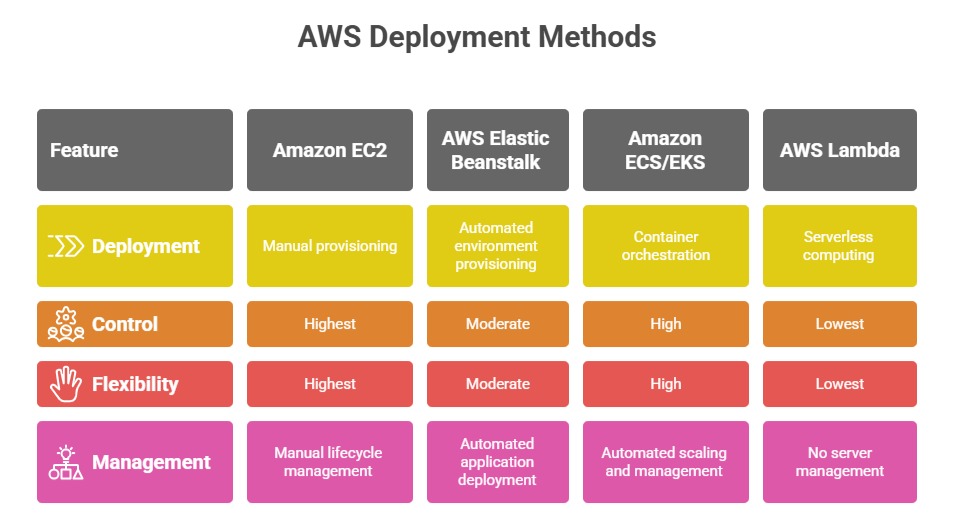
AWS offers multiple services like EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, and ECS that simplify the process for different types of applications. Understanding foundational deployment workflows helps users build, test, and launch applications in the cloud effectively.
Concepts of Basic AWS Application Deployment
Application deployment generally involves preparing the environment, provisioning necessary resources, deploying or uploading the application code, and managing configurations to ensure availability, scalability, and security.
AWS abstracts much of the traditional complexity by offering managed services and automation tools.
General Steps in Basic Application Deployment on AWS
The steps below outline a simplified workflow for setting up and managing applications in the AWS cloud environment.
1. Prepare the Environment: Create an AWS account and configure user access with IAM roles and policies to secure app resources.
2. Provision Infrastructure: Use the AWS Management Console, CLI, or CloudFormation templates to create computing instances (EC2), storage (S3, EBS), and networking (VPC, subnets, security groups).
3. Deploy Application Code: Upload application code manually via SSH (for EC2) or automatically through CI/CD pipelines, Elastic Beanstalk environments, or container repositories like Amazon ECR.
4. Configure Application and Services: Set environmental variables, load balancers, auto-scaling groups, and database connections for performance and reliability.
5. Monitor and Manage: Use AWS CloudWatch and CloudTrail to monitor application logs, performance metrics, and security events. Employ AWS Budgets and Cost Explorer to control resource expenditure.
Example: Deploying a Simple Web Application on EC2
1. Launch an EC2 instance with the desired OS and security groups configured.
2. Connect to the instance via SSH and install necessary software such as Apache, Nginx, or application runtimes.
3. Upload your application files using SCP or deploy via Git.
4. the web server and test application availability via the instance’s public IP.
5. Optionally, attach an Elastic IP and configure Route 53 for DNS routing.
