Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and log monitoring tools are vital components in modern Linux system security architectures. IDS detect unauthorized access, suspicious activities, and potential threats in real-time, while log monitoring systems provide continuous visibility into system events, aiding in incident detection, analysis, and compliance.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) monitors network traffic or host-level activities to identify malicious behavior or violations of security policies. Its primary role is to detect and alert administrators about potential security incidents so that timely investigation and response can take place.
While an IDS itself does not block or prevent traffic, it is commonly used alongside an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) to provide active defense and enhanced overall security.
Types of IDS
1. Network-based IDS (NIDS): Monitors network traffic for suspicious patterns. Installed on network segments.
2. Host-based IDS (HIDS): Monitors individual hosts for unusual activity such as file changes, login anomalies, or system calls.
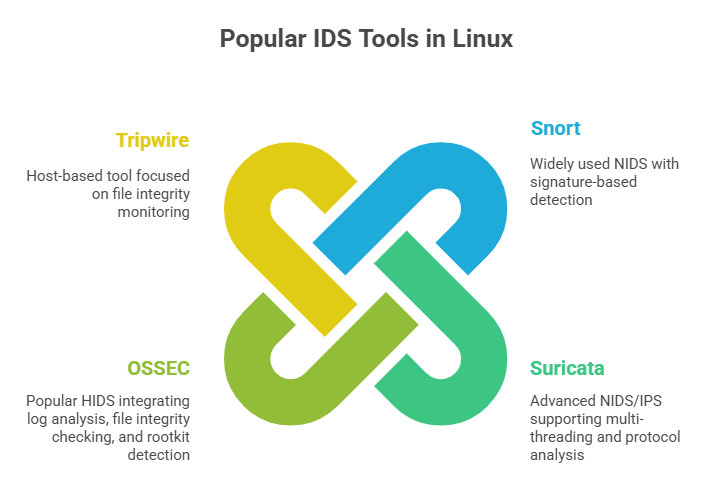
IDS Detection Techniques
1. Signature-based: Uses predefined patterns of known threats.
2. Anomaly-based: Detects deviations from normal behavior.
3. Hybrid: Combines signature and anomaly detection for enhanced accuracy.
Log Monitoring Tools
Log monitoring plays a critical role in continuously collecting, analyzing, and correlating logs from various system components to maintain visibility into system activity. By examining logged data, it helps detect signs of misuse, operational failures, or security-related events at an early stage.
Additionally, log monitoring supports compliance requirements and provides valuable evidence for forensic investigations during incident analysis.
Common Log Sources
1. System logs (e.g., /var/log/syslog, /var/log/auth.log)
2. Application logs
3. Network devices and firewalls
4. Security tools and IDS output
Popular Log Monitoring Solutions
1. Syslog-ng and rsyslog: Flexible and scalable syslog servers for capturing logs.
2. Elastic Stack (ELK): Combines Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana for real-time log analysis and visualization.
3. Graylog: Centralized log management and analysis platform.
4. Splunk: Commercial log analysis tool supporting extensive data ingestion and alerting.