Automated incident detection and response systems play a crucial role in modern cybersecurity by swiftly identifying threats and initiating mitigation measures without waiting for human intervention. These systems enhance organizational resilience by accelerating response times, reducing human errors, and enabling security teams to focus on complex investigations.
Case Study Highlights
The cases below illustrate the strategic value of automated security operations at scale. They demonstrate how automation supports proactive defense, compliance, and business continuity.
1. Automated Firewall Response to Malicious IPs
In a large enterprise environment, an automated system integrated with an intrusion detection system (IDS) was deployed to detect suspicious network traffic.
Upon identifying malicious IP addresses involved in scanning and attempted intrusions, the system automatically updated firewall rules to block those IPs in near real-time.
This significantly reduced the attack surface and prevented potential lateral movement within the network.
The automation allowed the security operations center (SOC) to prioritize complex threat investigations rather than manual firewall updates.
2. AI-Driven Threat Detection and Playbook Execution
A multinational corporation implemented AI-powered security orchestration and automated response (SOAR) tools that continuously monitored logs, network traffic, and endpoint telemetry.
Upon detecting anomalies or policy violations, the system triggered predefined playbooks—automated sequences of containment actions like isolating affected hosts, disabling compromised accounts, and blocking malicious domains.
This proactive containment minimized data exfiltration risk and downtime caused by ransomware and insider threats.
The AI continuously learned from incident response outcomes, optimizing rules and refining detection sensitivity.
3. Cloud Provider’s Incident Management Automation
A leading cloud service provider deployed automated incident detection tools that combined metrics monitoring, log analysis, and user behavior analytics to rapidly identify suspicious activities in customer workloads.
Security engineers were engaged automatically within minutes of critical alarms, while automated measures such as network segmentation and session termination were enacted to contain threats.
Integration with ticketing and case management systems ensured documented workflows and compliance.
This robust automation enabled scalable detection across millions of cloud instances with minimal false positives.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Automated Response in Healthcare
A healthcare organization utilized automated detection of anomalous system behavior and unauthorized access attempts on patient data systems.
On incident detection, automated alerts were sent to security staff, and suspected devices were isolated from the network automatically.
Forensic data was collected unobtrusively for rapid incident analysis.
Automation ensured HIPAA compliance through timely detection, response, and documentation.
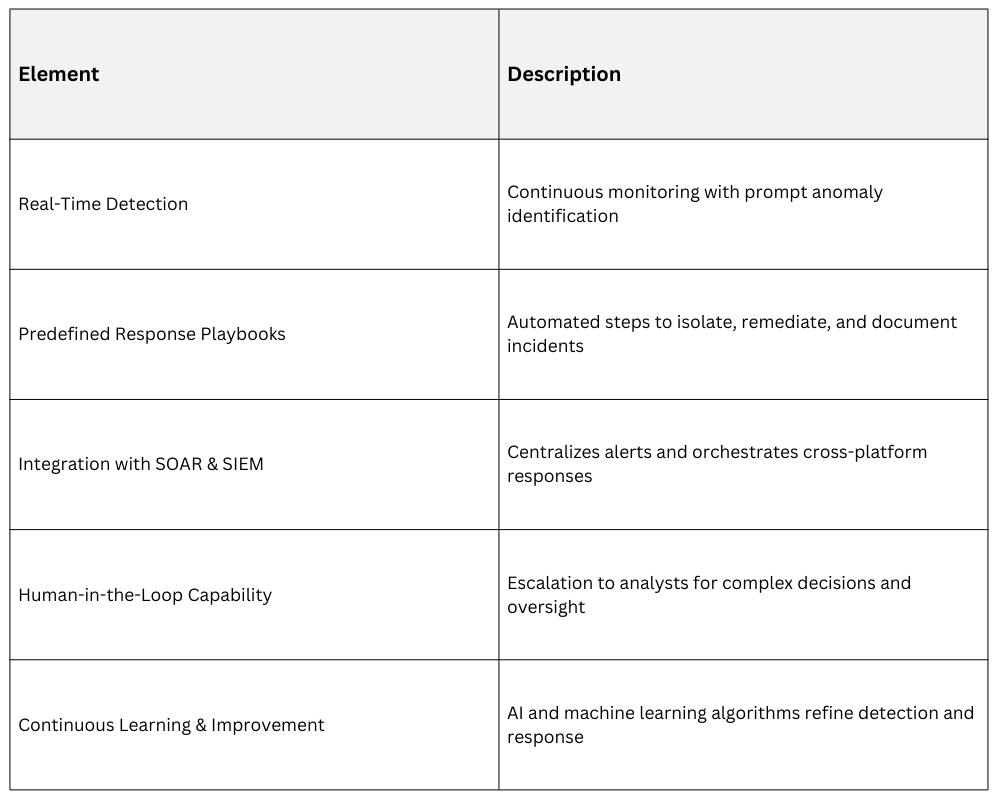
Common Elements of Successful Automation