Automated log analysis and alerting are essential practices in managing the security and health of Linux systems efficiently. By using scripts to sift through vast amounts of log data, system administrators can detect anomalies, errors, or security incidents quickly and trigger alerts for rapid response.
Importance of Automated Log Analysis
Implementing automated log analysis helps organizations maintain operational integrity and meet regulatory requirements. The following points highlight its role in detecting anomalies, reducing errors, and supporting compliance audits.
1. Logs contain critical information about system performance, user activity, and security events.
2. Manual log review is time-consuming and error-prone due to volume and complexity.
3. Automation enables real-time detection of events such as failed logins, suspicious access, or system errors.
4. Accelerates incident response and supports compliance monitoring.
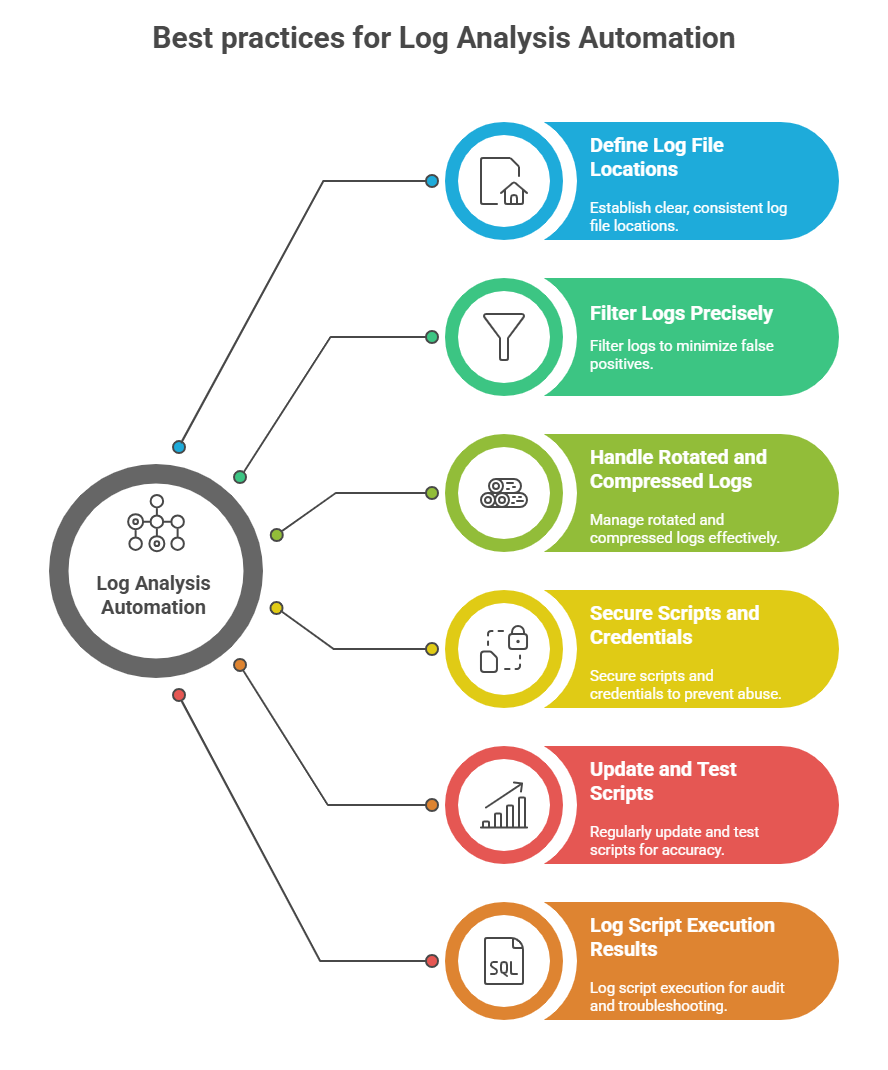
Core Techniques for Automated Log Analysis
Automated log analysis enables timely detection of security events and operational issues. The list below highlights techniques for filtering logs, analyzing recent activity, and identifying critical patterns.
Parsing Logs with Shell Tools
1. Use standard Unix utilities such as grep, awk, sed, and cut to filter and extract relevant log entries.
2. Example: Finding failed SSH login attempts:
grep "Failed password" /var/log/auth.log3. Pattern matching and regular expressions can identify specific events or keywords.
Using Log Rotation and Timestamps: Recent logs can be efficiently analyzed by integrating timestamps with filtering commands. Tools like tail or journalctl help preprocess logs, allowing focus on the newest data and improving the speed of log review.
Scripting Flexible Log Searches: Flexible log analysis can be achieved by combining parsing commands within Bash loops or functions to generate summaries and statistics. Conditional checks can be used to detect thresholds, such as when the number of failed login attempts exceeds a defined limit.
Implementing Alerting Mechanisms
Automated alerts enable proactive detection of security incidents and operational anomalies. The list below highlights techniques for sending notifications and integrating them with monitoring systems.
Alert Types
1. Email notifications using mail or sendmail.
2. SMS or messaging platform alerts using API integration.
3. System notifications using wall or custom dashboards.
Sample Alert Script
failed_logins=$(grep "Failed password" /var/log/auth.log | wc -l)
threshold=5
if [ "$failed_logins" -gt "$threshold" ]; then
echo "Alert: $failed_logins failed SSH login attempts detected." | mail -s "Security Alert" admin@example.com
fiAutomating Alert Execution: Alerts can be automated by scheduling scripts through cron or systemd timers to perform periodic scans. These scripts can be integrated with existing monitoring frameworks or SIEM systems to provide consolidated and timely alerting across the infrastructure.