Integrating shell scripts with security scanning tools enhances automated vulnerability assessment, compliance checks, and system hardening in Linux environments. By scripting the execution, reporting, and alerting of scans from tools like Lynis and OpenVAS, administrators can streamline regular security auditing and respond promptly to identified risks.
Lynis and OpenVAS
Lynis is a widely used open-source security auditing tool designed for Unix and Linux systems, focusing on local system assessments with a lightweight footprint. It performs compliance checks, vulnerability detection, and provides practical system hardening recommendations to improve overall security posture.
In contrast, OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System) is a comprehensive, network-oriented vulnerability scanner capable of conducting both authenticated and unauthenticated scans across large and diverse network environments. It delivers detailed vulnerability reports and integrates closely with the Greenbone Vulnerability Manager (GVM) for centralized management, analysis, and reporting.
Automating Lynis with Shell Scripts
The key goal of automating Lynis is to perform consistent, repeatable security audits without manual intervention. The points below outline a typical workflow, example scripting approach, and recommended best practices.
Typical Workflow
1. Execute Lynis scan with command:
lynis audit system --quiet2. Specify audit file and report locations.
3. Parse Lynis log or report files to extract warnings and suggestions.
Example Script Snippet
#!/bin/bash
REPORT="/var/log/lynis-report.dat"
lynis audit system --quiet --logfile $REPORT
if grep -q "WARNING" $REPORT; then
echo "Lynis warnings detected! Check $REPORT for details." | mail -s "Lynis Security Alert" admin@example.com
fiBest Practices: Running scans regularly through cron jobs or systemd timers to ensure continuous security assessment. Detailed logging should be enabled to support auditing, compliance, and troubleshooting activities. Additionally, customizing Lynis profiles for environment-specific checks helps ensure the scans are aligned with organizational policies and system requirements.
Integrating OpenVAS with Shell Scripts
Integrating OpenVAS with automation scripts supports repeatable scanning, audit readiness, and timely remediation. The list below highlights the scanning workflow, automation approach, and operational safeguards.
Running OpenVAS Scans: OpenVAS scans usually initiated via the GVM interface or command-line tools like omp or gvm-cli. Scripts can automate scan creation, start scans, check status, and fetch reports.
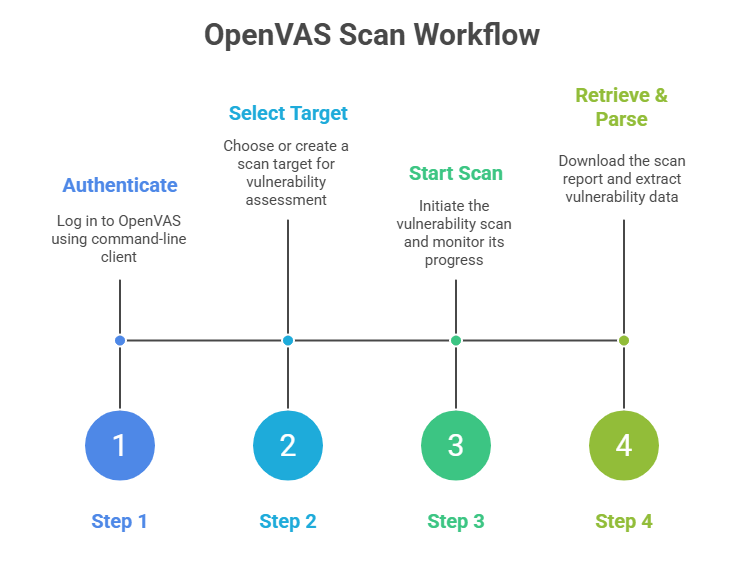
Example Pseudocode for Automation
# Authenticate and launch OpenVAS scan
gvm-cli ssh --gmp-username admin --gmp-password password << EOF
<create_target>...</create_target>
<start_task>...</start_task>
EOF
# Poll for completion and fetch report
# Parse report XML/JSON to summarize findingsBest Practices: Securely storing scan credentials in protected files or carefully managed environment variables to prevent unauthorized access. Scan automation should be integrated with change management processes and alerting systems to ensure findings are tracked and acted upon appropriately. Regularly updating OpenVAS vulnerability feeds is essential to maintain accurate and reliable detection of current security risks.
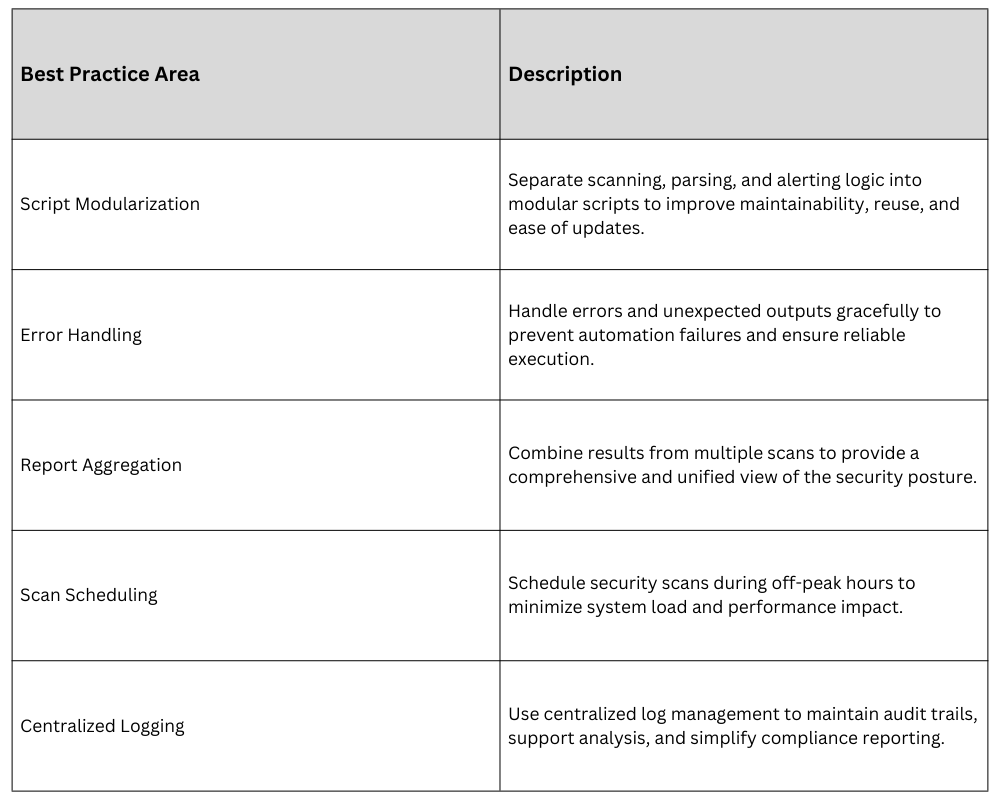
Overall Best Practices for Integration
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
