The core principles of generative modeling focus on how models learn the underlying data distribution in order to generate new, realistic samples. Likelihood-based approaches train models by explicitly estimating the probability of the observed data, allowing direct evaluation of how well the model fits the data.
Score-based approaches, in contrast, learn the gradients of the data distribution and generate samples through iterative refinement processes, offering an alternative way to model complex data without directly
Likelihood-Based Generative Models
Likelihood-based models learn to directly estimate the probability density of the data distribution, allowing them to generate samples by maximizing the likelihood of observed data.
These approaches excel in capturing explicit probabilities, making them intuitive for tasks requiring precise density estimation, such as anomaly detection or data imputation.
Key Principles and Mechanisms
At their core, likelihood-based models define a parametric probability distribution with learnable parameters and train by maximizing the log-likelihood over training data.
This explicit modeling contrasts with implicit methods, enabling exact evaluation of how likely a sample is under the model.
.png)
Consider a practical example: In language modeling with GPT architectures, likelihood-based training predicts the next token conditionally on previous ones, enabling coherent story generation from prompts.
Main Architectures
Likelihood-based methods span several architectures, each balancing expressiveness with computational tractability.
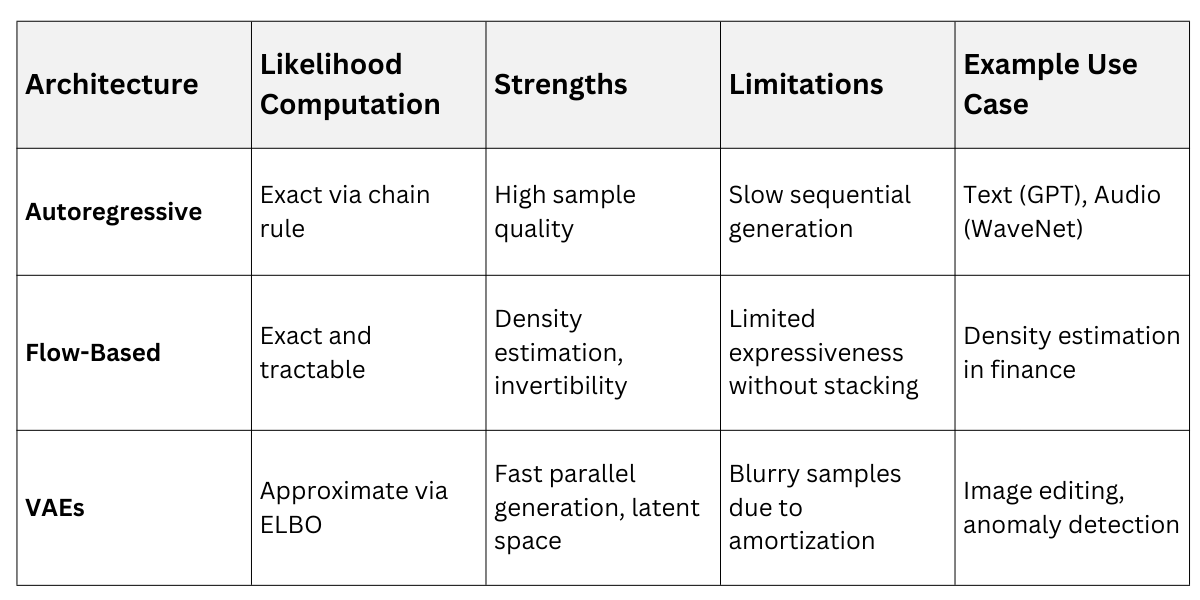
These models shine in scenarios needing probabilistic reasoning, like Bayesian inference in healthcare for generating synthetic patient records.
Score-Based Generative Models
Score-based models, also known as score-matching or diffusion models, learn the score function—the gradient of the log-probability density—rather than the density itself.
This implicit approach has surged in popularity since 2020, underpinning state-of-the-art image and video generators like Stable Diffusion, due to superior sample quality and robustness.
Core Principles: Diffusion and Score Matching
Diffusion models simulate a forward process that gradually adds noise to data, turning clean samples into pure noise over many steps. The reverse process learns to denoise step-by-step, guided by an estimated score that points toward higher data density.
Score matching minimizes the difference between the model's score and the true data score, often via a denoising objective for efficiency: the model predicts added noise given a noisy sample and timestep.
.png)
A practical example: Training Stable Diffusion on LAION-5B dataset learns scores for text-conditioned image generation, allowing prompts like "a cyberpunk Delhi skyline at dusk" to produce photorealistic outputs.
Advantages and Evolution
Score-based models outperform likelihood-based ones in high dimensions, avoiding issues like mode collapse.
Key Strengths
1. Exceptional sample quality via gradual refinement.
2. Conditional generation integrates seamlessly, such as classifier-free guidance.
3. Scalable to massive datasets with U-Net backbones.
Recent advances as of 2025 include
1. Flow Matching: Straightens diffusion paths for fewer steps.
2. Consistency Models: Distill diffusion into one-step generators.
3. Rectified Flows: Optimize transport paths for efficiency.
In practice, score-based models dominate creative AI, like Midjourney's hyper-realistic art, due to their stability on web-scale data.
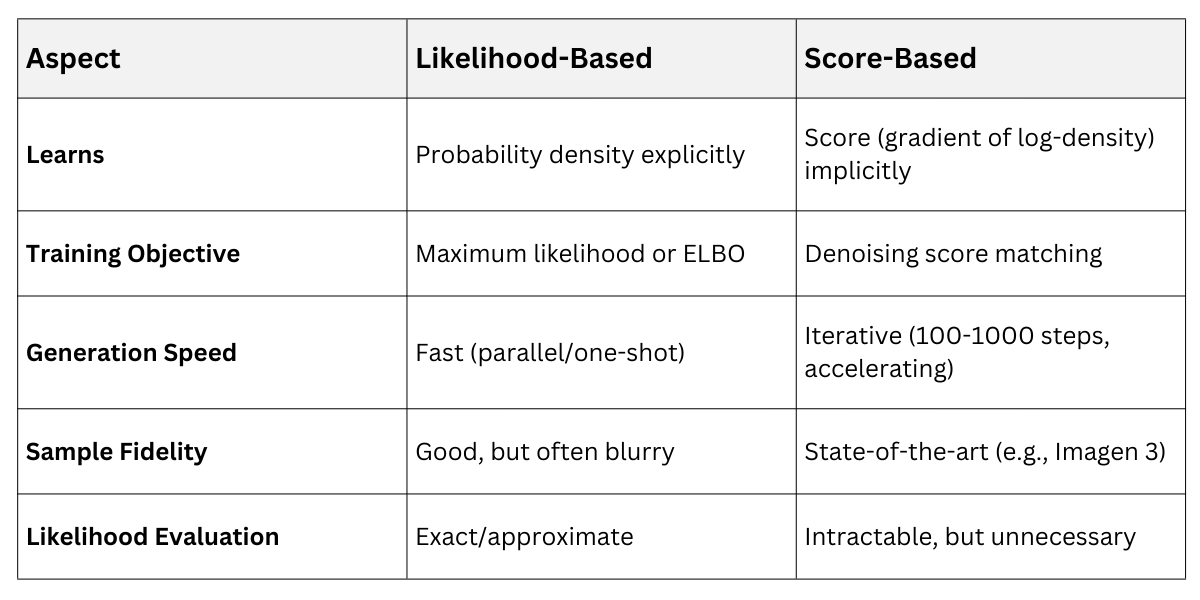
Comparing Likelihood-Based and Score-Based Approaches
Choosing between these paradigms depends on your goals—likelihood for explicit probabilities, score for visual realism. Both maximize data likelihood indirectly but differ in mechanics and trade-offs.
Likelihood-Based Vs Score-Based
Likelihood models offer tractable densities, ideal for downstream tasks like classification via Bayes rule. Score models prioritize perceptual quality, leveraging perturbation stability.
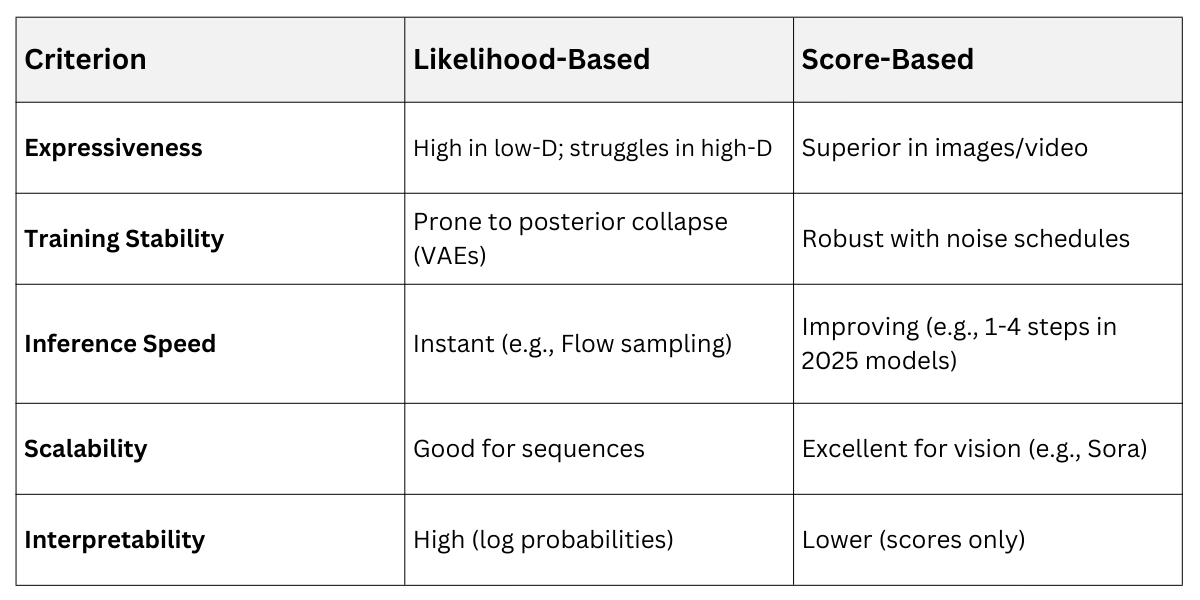
Hybrid Example: GLIDE combines autoregressive priors with diffusion for text-to-image, blending strengths.
In course projects, use likelihood for prompt design in LLMs, such as next-token prediction, and score for visual architectures like DiT (Diffusion Transformers).
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
