Deploying AI systems in production requires more than model accuracy—it demands reliability, scalability, and observability.
API integration ensures seamless interaction between models and applications, while rate limiting protects services from overload and abuse.
Monitoring best practices provide continuous visibility into system performance, errors, and model behavior, enabling teams to maintain stability and quickly respond to issues in real-world environments.
API Integration Fundamentals
API integration forms the backbone of deploying Generative AI systems, connecting your custom architectures—such as prompt-engineered pipelines or fine-tuned models—to external services like cloud inference engines or vector databases.
Proper integration ensures seamless data flow while minimizing latency and errors, which is critical for AI apps where response times directly impact user experience.
Start by selecting RESTful APIs or GraphQL for flexibility in querying AI model outputs. Key steps include authenticating requests, handling payloads in JSON format, and validating responses before processing them in your AI pipeline.
1. Authentication methods: Use API keys for simplicity in development, OAuth 2.0 for user-delegated access, or JWT tokens for stateless sessions in production.
2. Payload optimization: Structure prompts as JSON objects with fields like model, prompt, max_tokens, and temperature to leverage provider-specific features.
3. Idempotency: Add unique request IDs to prevent duplicate processing during retries, especially useful for costly AI generations.
Here's a practical Python example using the requests library for integrating with a hypothetical GenAI API:
import requests
import json
def generate_text(api_key, prompt, model="gpt-4o"):
url = "https://api.genai-provider.com/v1/completions"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"model": model,
"prompt": prompt,
"max_tokens": 150,
"temperature": 0.7
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()["choices"][0]["text"]
else:
raise ValueError(f"API error: {response.text}")This code demonstrates secure header usage and basic error catching, aligning with industry standards like those from OpenAI or Anthropic APIs.
Rate Limiting Strategies
Rate limiting protects both your application and upstream AI providers from overload, enforcing quotas on requests per minute, hour, or day to maintain stability.
In Generative AI deployments, where token-based pricing and compute-intensive inferences prevail, effective rate limiting prevents throttling, reduces costs, and ensures fair resource allocation across users.
Implement client-side and server-side limiting to handle bursty traffic from concurrent prompt generations. Common algorithms include fixed-window counters for simplicity and token bucket for smoothing spikes.
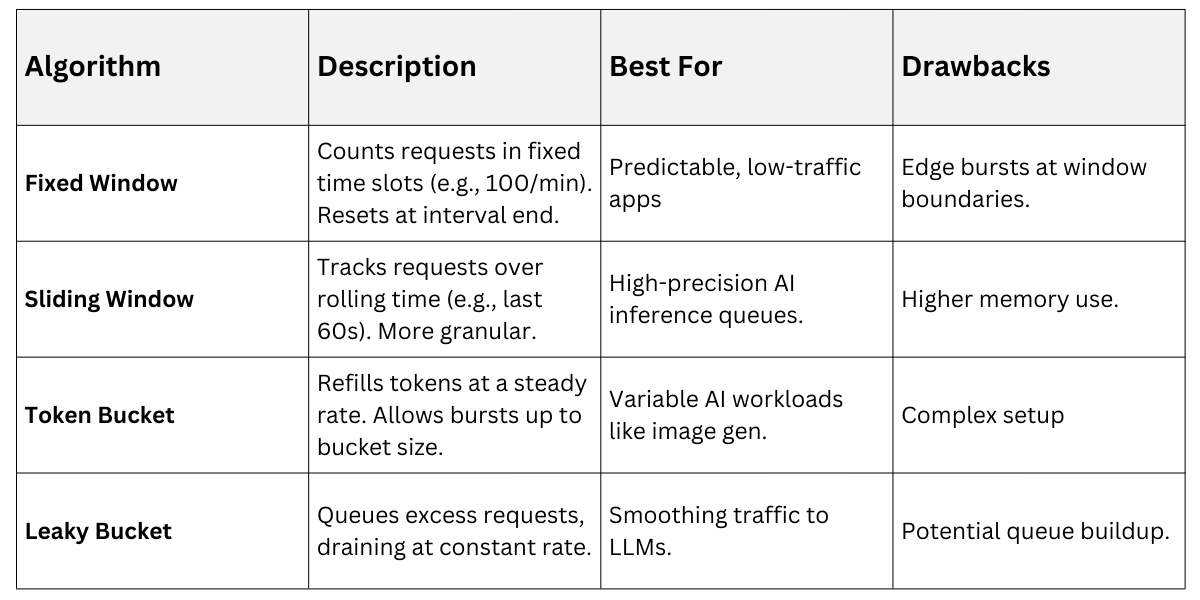
To enforce limits in code, use libraries like ratelimit in Python:
1. Install via pip install ratelimit.
2. Decorate your API call function: @ratelimit.sleep_and_retry(100, rate=60) for 100 calls per minute.
3. Monitor remaining quota via response headers like X-RateLimit-Remaining.
For GenAI specifics, respect provider limits—e.g., OpenAI's 10k TPM (tokens per minute)—and implement exponential backoff: wait 1s, then 2s, 4s on 429 errors.
Monitoring Best Practices
Monitoring provides visibility into your deployed AI system's health, tracking metrics like latency, error rates, and token usage to catch issues early.
For Generative AI, where outputs can vary wildly due to prompt sensitivity or model hallucinations, comprehensive observability ensures quick debugging and optimization.
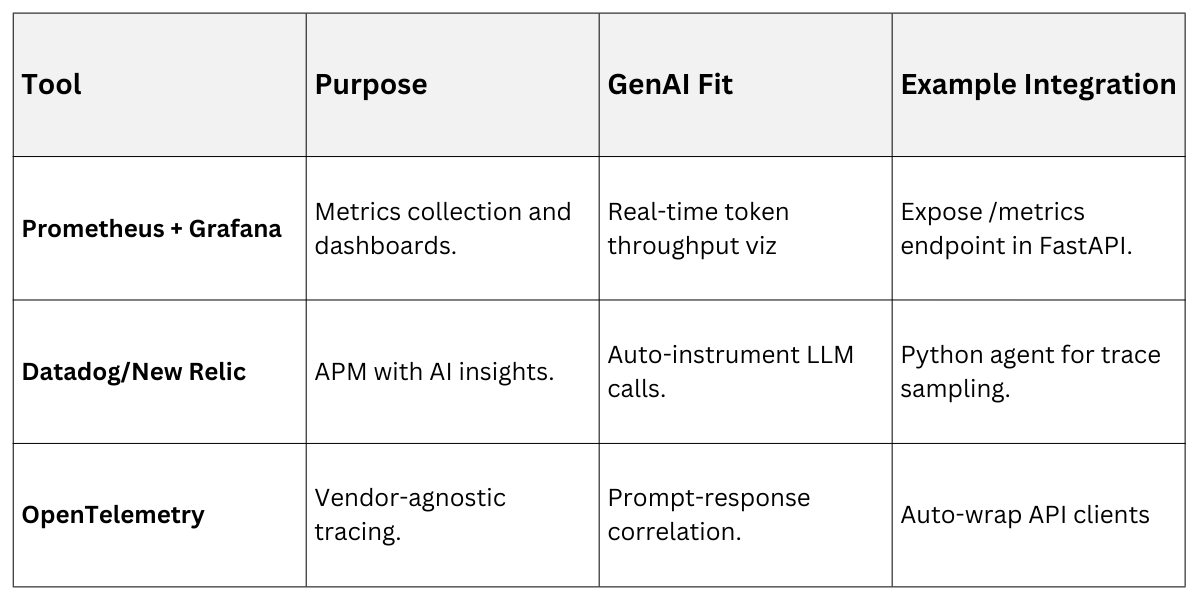
Combine logging, metrics, and tracing for full coverage. Tools like Prometheus for metrics, ELK stack for logs, and Jaeger for distributed tracing integrate well with Kubernetes-based deployments.
Key Metrics to Monitor
1. Request latency (p50/p95 percentiles).
2. Error rates (5xx, 429s).
3. AI-specific: Tokens generated, hallucination scores via semantic checks.
4. Cost: Cumulative API spend.
Set up alerts for anomalies, such as latency spikes indicating rate limit hits.
In practice, log structured data
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.info("AI Generation", extra={
"prompt_length": len(prompt),
"tokens_used": response_tokens,
"latency_ms": end_time - start_time
})Proactive monitoring caught a 40% cost overrun in a recent production chatbot by alerting on excessive verbose prompts.
Security and Error Handling in Production
Secure integrations mitigate risks like credential leaks or injection attacks, vital for AI systems processing sensitive prompts.
Pair this with robust error handling to gracefully degrade during outages, maintaining user trust.
Use environment variables for secrets (e.g., os.getenv('API_KEY')) and HTTPS everywhere. Implement circuit breakers: pause calls after failures, fallback to cached responses.
Error Handling Flow
.png)
For AI, validate outputs against schemas to filter unsafe generations, explaining terms like prompt injection—where malicious inputs hijack model behavior.
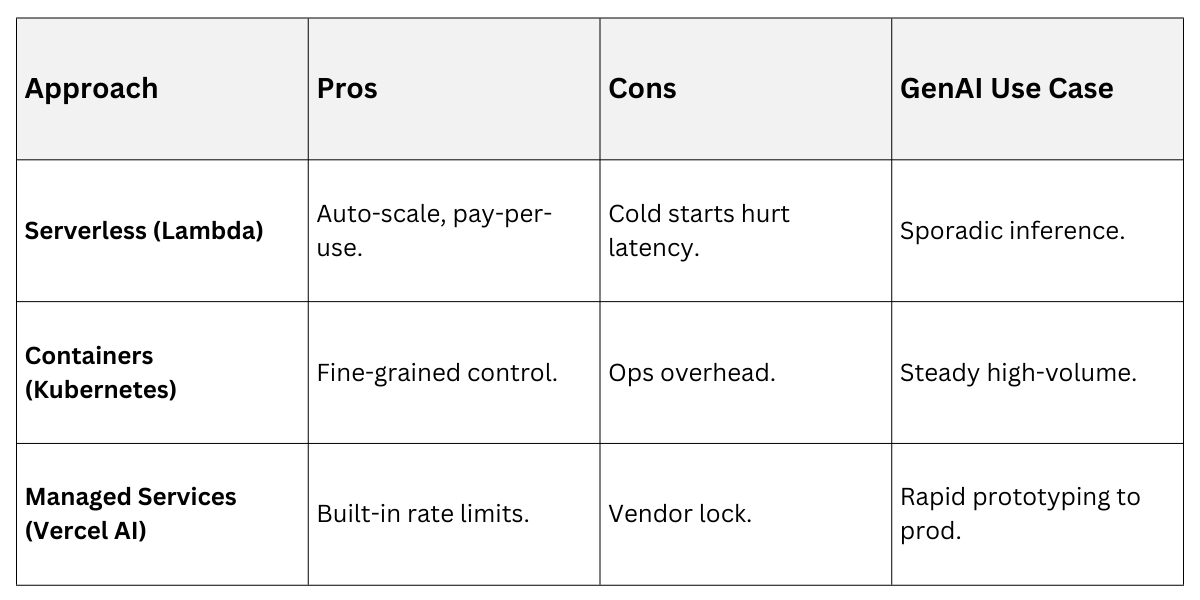
Scaling and Optimization Tips
Scale deployments horizontally with load balancers and auto-scaling groups in AWS/GCP. Optimize by batching requests (e.g., 10 prompts at once) and caching frequent responses with Redis.
Compare Scaling Approaches
These practices ensure your GenAI architecture handles Black Friday-like spikes without crumbling.