As prompt engineering becomes critical for achieving high-quality outputs from large language models, Automatic Prompt Optimization (APO) techniques such as Automatic Prompt Engineering (APE) and Optimization by PROmpting (OPRO) have emerged to reduce manual effort.
These methods automatically generate, evaluate, and refine prompts to maximize model performance on specific tasks.
Meta-prompting complements this approach by using prompts that instruct the model on how to generate, evaluate, or improve other prompts, enabling self-improvement and adaptability.
Core Concepts
These techniques shift prompt engineering from an art to a systematic process, leveraging LLMs themselves to generate and improve prompts.
APE automates instruction creation by producing multiple candidates from task examples, evaluating them, and selecting the best performer. OPRO takes an iterative approach, using a meta-prompt with past results to evolve better prompts over cycles.
Meta-prompting operates at a higher level, where prompts generate or refine other prompts dynamically based on context or feedback.
Automatic Prompt Engineer (APE)
APE frames prompt optimization as an automated search problem, ideal for zero-shot or few-shot scenarios where examples define the task.
The process starts with an LLM generating diverse instruction candidates in forward or reverse modes—forward infers directly from examples, while reverse generates from desired outputs.
Candidates run on a target model, and scores from a separate evaluator pick the winner, often outperforming hand-crafted prompts like "Let's think step by step.".
Key Steps
1. Provide task demonstrations (input-output pairs) to an inference LLM.
2. Generate 50-100 instruction candidates via zero-shot prompting.
3. Execute candidates on the target LLM and score using an evaluator model.
4. Select and deploy the highest-scoring prompt.
Practical Example: For sentiment analysis, APE might generate "Classify the emotion in this text as positive, negative, or neutral, considering sarcasm" from review examples, boosting accuracy by 5-10% over basics.
Optimization by Prompting (OPRO)
Developed by DeepMind, OPRO treats prompt creation as an optimization task solved entirely by LLMs, excelling in math and reasoning benchmarks.
It uses a meta-prompt that includes the task, validation set, prior prompts, and their scores to guide generation of superior candidates iteratively.
Unlike one-shot generation, OPRO builds a trajectory of improvements, converging when no better prompt emerges, often gaining 8% on GSM8K or 50% on Big-Bench Hard over humans.
The workflow follows these Numbered Steps
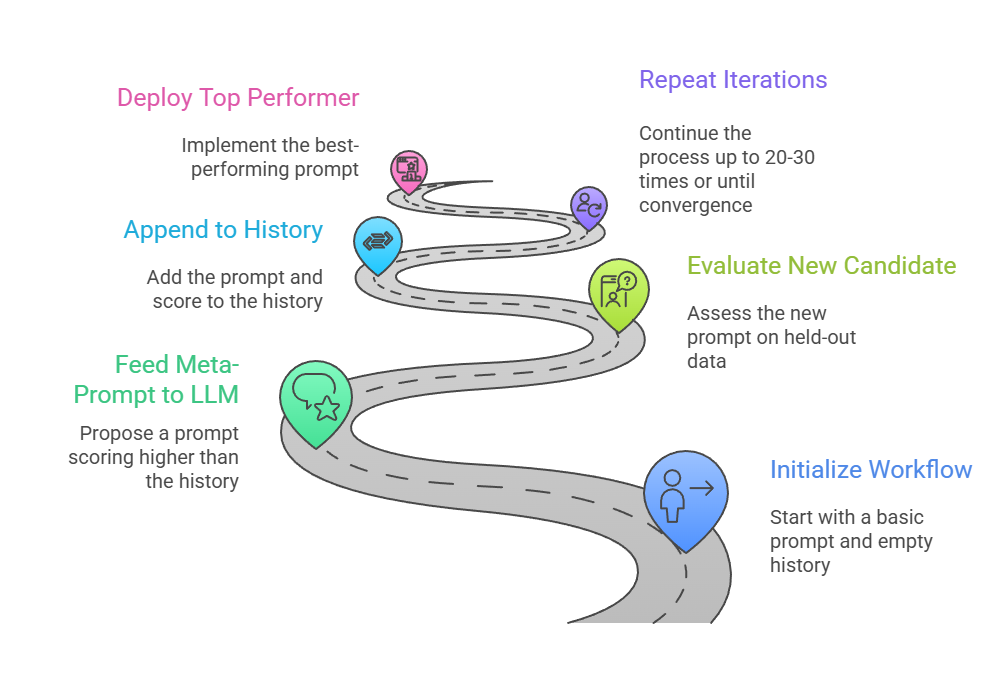 Example in Action: Starting with "Solve this math problem," OPRO evolves to "Break down the equation step-by-step, verifying each operation, then compute the final answer," improving solve rates significantly.
Example in Action: Starting with "Solve this math problem," OPRO evolves to "Break down the equation step-by-step, verifying each operation, then compute the final answer," improving solve rates significantly.
Meta-Prompting Techniques
Meta-prompting elevates LLMs to "prompt architects," generating task-specific prompts on-the-fly for adaptability.
This method emphasizes prompt structure over content, using one LLM instance to craft prompts for another, enabling self-improvement loops like recursive refinement.
It shines in dynamic scenarios, reducing tokens while adapting to feedback, and supports multi-stage processes like breaking complex tasks into subtasks.
Common Applications Feature:
1. Prompt generation: "Create a prompt for analyzing climate impacts, including short/long-term effects."
2. Refinement: "Improve this prompt [original] based on poor outputs [examples]."
3. Task decomposition: "Generate subtasks and prompts for market analysis."
Real-world use: In education, a meta-prompt like "Design a step-by-step tutoring prompt for quadratic equations" yields adaptive learner guides.
APE, OPRO, and Meta-Prompting
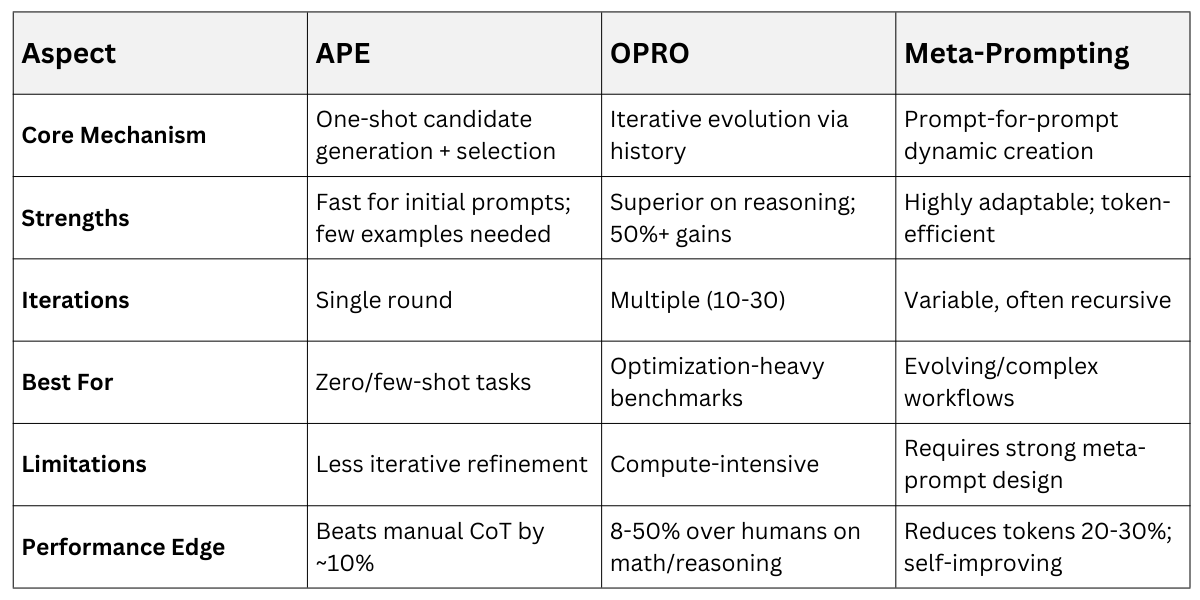
APE suits quick setups, OPRO deep optimization, and meta-prompting flexible chaining.
Practical Implementation and Best Practices
Implement these in Python with LLM APIs like OpenAI or Grok, starting small to validate.
Code snippet for basic APE (using pseudocode for clarity)
def ape_optimize(task_examples, llm):
candidates = llm.generate("Create instructions for: " + str(task_examples))
scores = []
for cand in candidates:
outputs = llm.run(cand, test_inputs)
score = evaluator(outputs, test_labels)
scores.append(score)
return candidates[argmax(scores)]Adapt for OPRO by looping with history accumulation.
Best Practices
.png)
Example workflow: Optimize a code generation prompt—APE generates 20 variants, OPRO refines top 5, meta-prompting adapts for new languages.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
