Vision-Language Models (VLMs), such as CLIP and Flamingo, are AI models designed to understand and connect visual and textual information. They learn joint representations of images and text, enabling tasks like image captioning, text-to-image retrieval, and zero-shot classification.
Unified Architectures, such as Emu and Kosmos, take this a step further by integrating multiple modalities (vision, language, and sometimes other inputs) into a single model.
This allows seamless handling of complex multimodal tasks without separate models for each modality, simplifying deployment and improving performance across diverse tasks.
Core Concepts in Vision-Language Fusion
Vision-language models process images and text jointly, learning shared representations that allow a single model to handle tasks like classification, retrieval, and generation across modalities. This fusion unlocks generative capabilities central to modern AI pipelines.
By understanding these foundations, you'll design prompts that leverage visual context for more accurate and creative outputs, a skill essential for deploying production-ready generative systems.
Contrastive Learning: The CLIP Paradigm
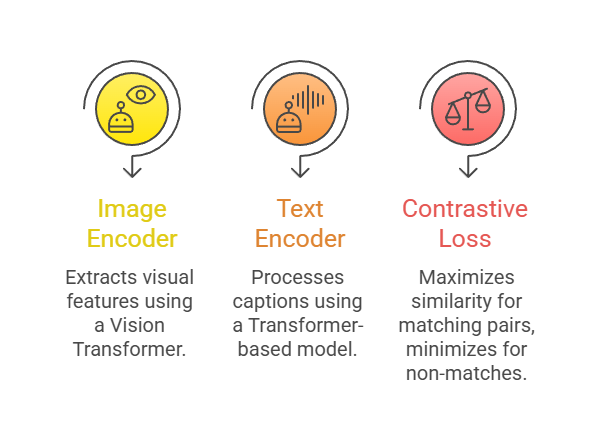
CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining), developed by OpenAI in 2021, revolutionized multimodal AI by training on 400 million image-text pairs via contrastive learning.
It encodes images and text into a shared embedding space, enabling zero-shot tasks without task-specific fine-tuning.
This approach excels in flexibility: given a text prompt like "a photo of a red sports car," CLIP computes similarity scores against images, ranking matches without retraining.
Key Components
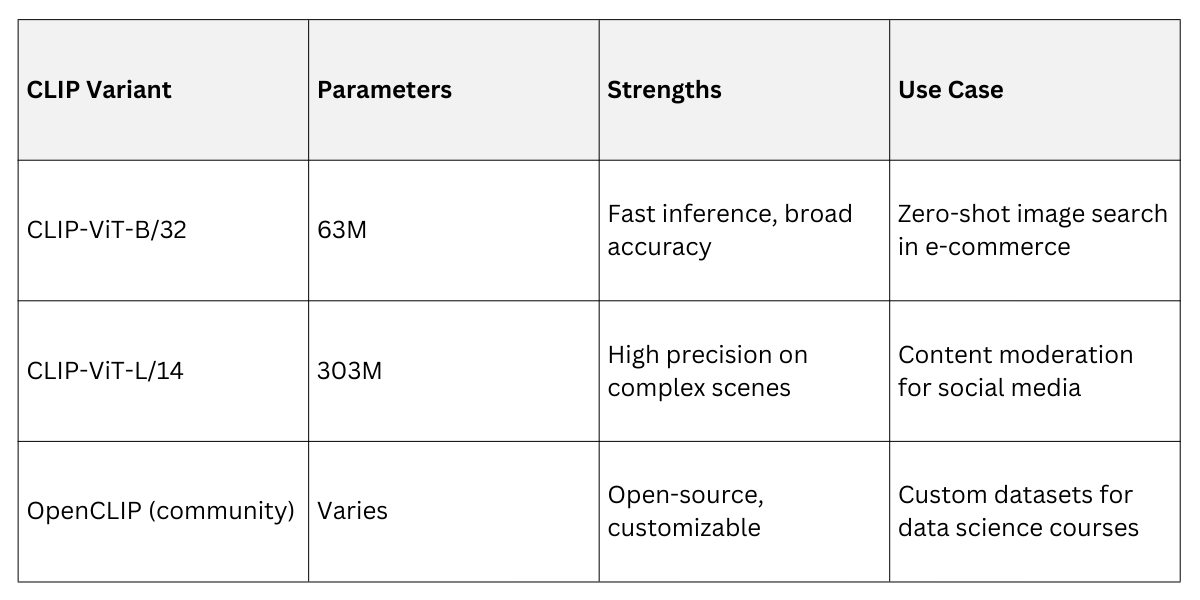
Practical Example: In a Python web app using Flask, load CLIP via openai/clip-vit-base-patch32 from Hugging Face to classify user-uploaded images against custom prompts, such as detecting "medical anomalies" in X-rays for a telemedicine dashboard.
To implement zero-shot classification in code
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPModel
import torch
from PIL import Image
model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32")
image = Image.open("your_image.jpg")
texts = ["a dog", "a cat", "a car"]
inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
outputs = model(**inputs)
probs = outputs.logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1)
print(probs) # Highest probability indicates best matchThis snippet integrates seamlessly into Django views for real-time image tagging.
Perceiver-Based Architectures: Flamingo in Action
Flamingo, released by DeepMind in 2022, builds on CLIP by introducing perceiver resamplers to handle long visual sequences efficiently, scaling to billion-parameter models for few-shot learning.
It freezes pretrained vision (like CLIP) and language models, adding lightweight adapters for multimodal fusion—ideal for generative tasks where prompts guide image-conditioned text generation.
Advantages Over CLIP
1. Supports in-context learning: Learns from few image-text examples in prompts.
2. Handles interleaved inputs: Text and images mixed in sequences.
For instance, in a data visualization course tool, prompt Flamingo with charts and text like "Describe trends in this sales graph," generating explanatory narratives for interactive dashboards.
Implementation Tip: Use Hugging Face's google/flamingo-base (experimental) in a Streamlit app for quick prototyping
# Pseudo-code for Flamingo inference (requires access to model)
prompt = "<image>Describe the key patterns in this plot."
output = model.generate(prompt) # Yields detailed captionUnified Architectures: Emu and Kosmos for End-to-End Generation
Unified architectures like Emu and Kosmos take multimodality further by treating all data—images, text, and even video—as tokenized sequences in a single autoregressive model. This enables true generative unity, where prompts seamlessly blend modalities.
These models shine in prompt design, as they interpret "draw a lion in a forest based on this description" to output rendered images or grounded text.
Emu: Scalable Image-Text Generation
Emu (from Meta, 2023 iterations like Emu2) employs a Unified Visual Token Representation with discrete tokens for images, allowing a language model to "speak" visuals.
It excels in high-fidelity generation from text prompts, outperforming diffusion models in speed.
1. Tokenize Input: Convert image patches to discrete codes via a VQ-VAE.
2. Autoregressive Decoding: Next-token prediction generates text or image tokens.
3. Prompt Conditioning: Embed text to steer generation.
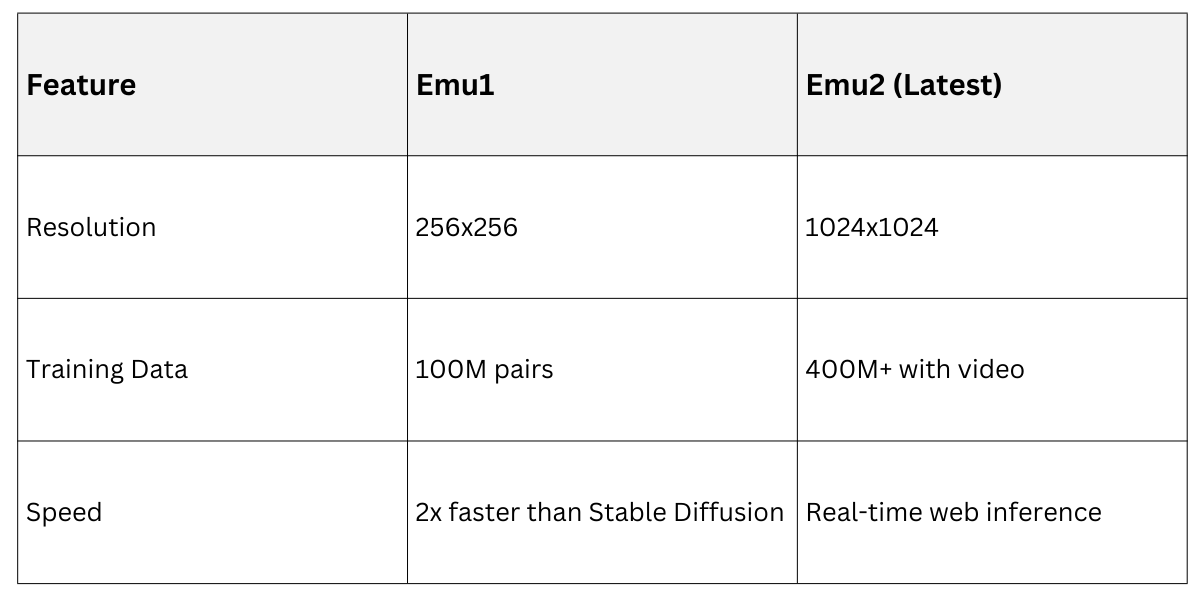
Example: In FastAPI endpoints, use Emu for dynamic thumbnails: POST a product description, GET generated visuals.
Kosmos: Grounding and Multimodal Reasoning
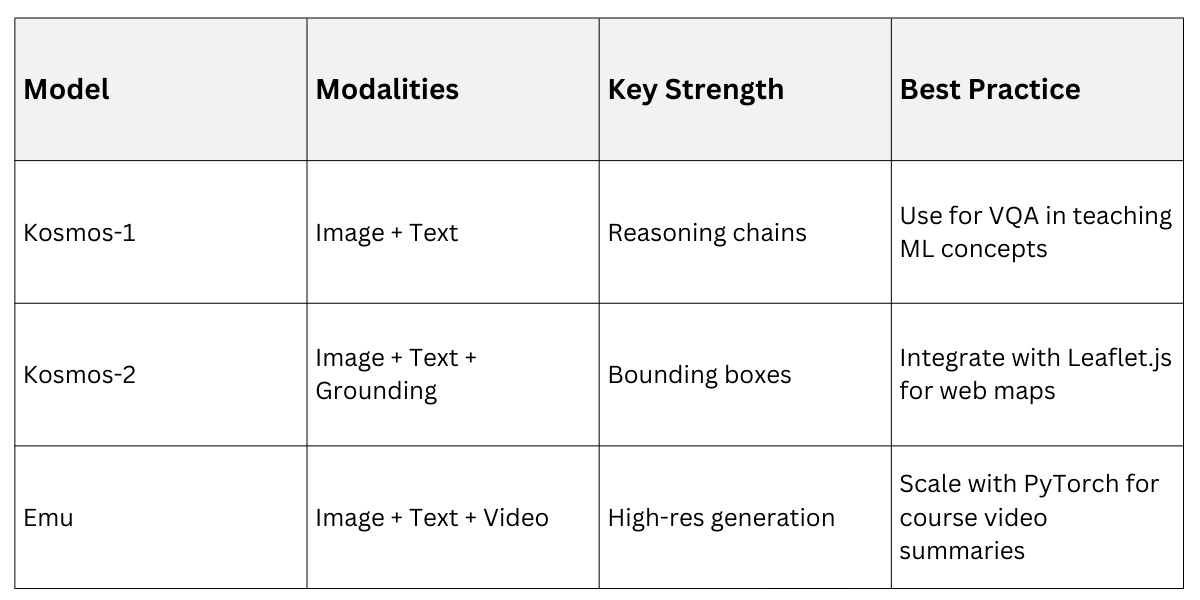
Kosmos-1 (Microsoft, 2023) and its successors like Kosmos-2 introduce grounding tokens to link text spans to image regions, enabling tasks like visual question answering (VQA) with precise localization.
Kosmos processes raw pixels alongside text, outputting interleaved responses—perfect for educational apps explaining code visualizations.
Core Innovations
1. Magneto-Emotion Embeddings: Blend modalities without heavy fusion layers.
2. Grounded Outputs: Phrases like "the red car [bbox: coords]" for interactive UIs.
Practical App: Build a Jupyter-based tool for data science students—upload a plot, prompt "Explain the outlier in top-right quadrant," and get reasoned, grounded analysis.
 Prompt Design Strategies for These Architectures
Prompt Design Strategies for These Architectures
Effective prompting maximizes these models' potential, especially in generative pipelines. Start with descriptive, modality-aware prompts: "Given this scatter plot [image], list top correlations."
Best Practices
.png)
In your Python projects, combine with LangChain: chain = CLIPRetriever | FlamingoGenerator for end-to-end web services.
Integration in Generative AI Workflows
These models fit into broader architectures via APIs like Hugging Face Inference Endpoints.
For a Django course platform
1. User uploads image + prompt.
2. CLIP scores relevance.
3. Kosmos generates grounded explanation.
4. Emu creates follow-up visuals.
This workflow supports scalable data science education, from auto-grading visualizations to personalized tutorials.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
