As prompt engineering becomes critical for achieving high-quality outputs from large language models, Automatic Prompt Optimization (APO) techniques such as Automatic Prompt Engineering (APE) and Optimization by PROmpting (OPRO) have emerged to reduce manual effort.
These methods automatically generate, evaluate, and refine prompts to maximize model performance on specific tasks.
Meta-prompting complements this approach by using prompts that instruct the model on how to generate, evaluate, or improve other prompts, enabling self-improvement and adaptability.
Core Concepts
Domain-specific adaptation refines large language models (LLMs) for particular fields using methods like fine-tuning or parameter-efficient techniques.
These ensure outputs align with industry norms, vocabulary, and constraints. This section explores foundational ideas central to generative AI architectures.
Key Techniques
.png)
Transfer learning underpins these, shifting knowledge from broad training to targeted use cases.
Adaptation Techniques
Various methods adapt models efficiently, balancing performance and cost. Each suits different scenarios in prompt design and architecture tweaks.
Fine-Tuning Approaches
Full fine-tuning trains all parameters but demands high compute. Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) uses labeled domain data to boost accuracy in tasks like code generation.
1. Prepare domain-specific dataset (e.g., code repositories).
2. Train with low learning rate to preserve base knowledge.
3. Evaluate on held-out domain tasks.
Benefits: High accuracy; Drawbacks: Resource-heavy.
Parameter-Efficient Methods
Techniques like LoRA insert small trainable adapters, updating under 1% of parameters.
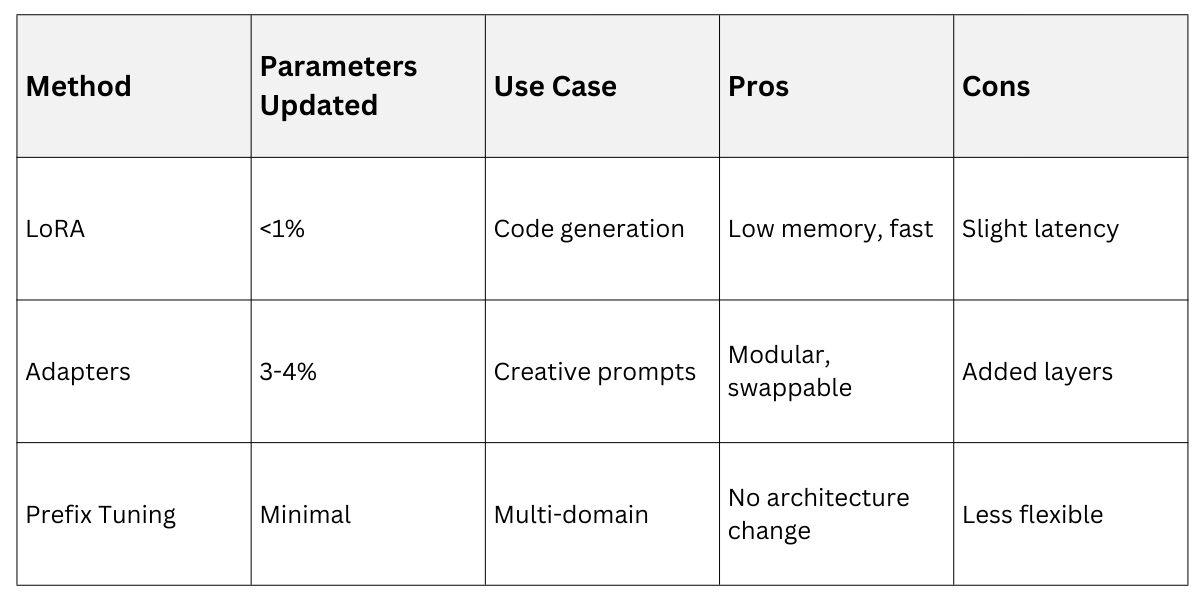
These enable quick swaps for domains like finance or healthcare.
Code Generation Adaptation
Code generation demands syntax accuracy, efficiency, and context awareness. Adaptation uses domain codebases to produce functional, idiomatic outputs.
Start with retrieval from project repos, then prompt the model. Tools like kNM-LM integrate in-domain code via Bayesian inference without fine-tuning.
Prompt Best Practices
1. Specify language, libraries, and constraints (e.g., "Python function for merge sort, O(n log n), handle empty lists").
2. Use chain-of-thought: "Explain approach, write pseudocode, then implement."
3. Include edge cases and tests for robustness.
Example Prompt: "Write a Flask API endpoint for user authentication using JWT. Include error handling, input validation, and unit tests. Follow PEP 8."
Outcomes: Reduces errors by 68% with detailed specs. and improves readability and security via SFT.
In practice, adapt models like CodeGPT for intra-project completion.
Creative Writing Prompts
Creative writing adaptation focuses on voice, originality, and narrative flow. Tailored prompts guide models to mimic styles or genres effectively.
Incorporate role-playing and constraints for consistency. RAG pulls from literary corpora for inspiration.
Effective Strategies
1. Define persona: "Act as a horror novelist like Stephen King."
2. Set structure: "Inciting incident, rising action, three alternative endings."
3. Add sensory details: "150 words, first-person, vivid tension."
Example: "Craft a sci-fi short story prompt: Dystopian city, AI protagonist rebels against human overlords. Emotional arc: Discovery to sacrifice. 300 words."
Domain Tweaks
1. Multi-turn for revisions: "Rewrite with more suspense."
2. Ethical alignment : via RLHF for safe, original content.
This yields engaging, human-like narratives suited for content creators.
Comparisons of Methods
Choosing adaptation depends on resources and task needs. Here's a structured overview for code vs. creative writing.
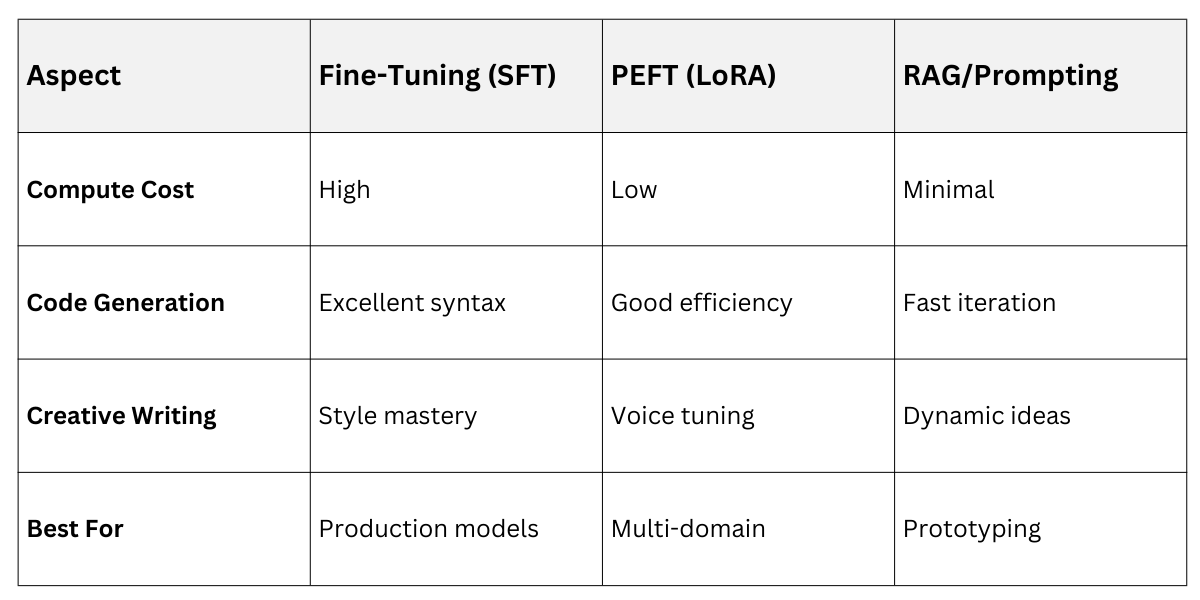
Hybrid approaches, like PEFT + RAG, optimize for both examples.
Practical Implementation of Model Adaptation
Apply adaptation systematically in your projects. Follow this process for reproducible results.
1. Assess Needs: Identify domain gaps (e.g., Python web dev for code).
2. Gather Data: Curate 1k-10k examples; augment synthetically.
3. Select Method: PEFT for efficiency, full-tune for precision.
4. Design Prompts: Test iteratively with specifics.
5. Evaluate: Use metrics like BLEU for code, human review for writing.
6. Deploy: Monitor with continual learning.
Code snippet for LoRA setup (pseudocode)
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
config = LoraConfig(r=16, lora_alpha=32)
model = get_peft_model(base_model, config)
# Train on domain dataThis workflow aligns with industry standards.
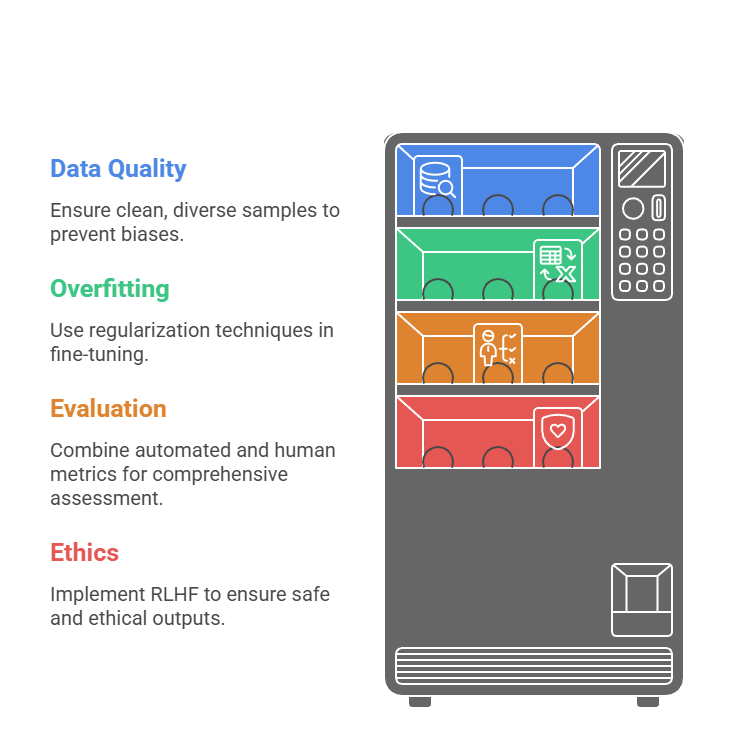
Challenges and Best Practices
Adaptation faces hurdles like data scarcity and hallucination. Mitigate with curation and feedback loops.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
