Agentic architectures for multimodal reasoning refer to AI systems that are composed of one or more autonomous agents capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting across multiple modalities such as text, images, audio, and video.
In multi-agent systems with tool use, individual agents can collaborate, delegate tasks, and interact with external tools (e.g., search engines, code execution environments, APIs) to solve complex problems.
These architectures emphasize planning, memory, feedback loops, and coordination, enabling more flexible and goal-directed reasoning compared to single-pass models.
Core Concepts of Agentic Architectures
Agentic architectures empower AI to go beyond one-shot responses, treating reasoning as an iterative process. At their heart, they integrate large language models (LLMs) with planning, memory, and execution loops for multimodal tasks.
Multimodal reasoning refers to processing diverse data types together—think combining a photo of a damaged car with a textual insurance claim.
Multi-agent systems distribute this workload across specialized agents, each handling a modality or subtask, while tool use lets them interact with external APIs, databases, or code interpreters for grounded actions.
Defining Key Components
These systems rely on modular building blocks that work in concert:
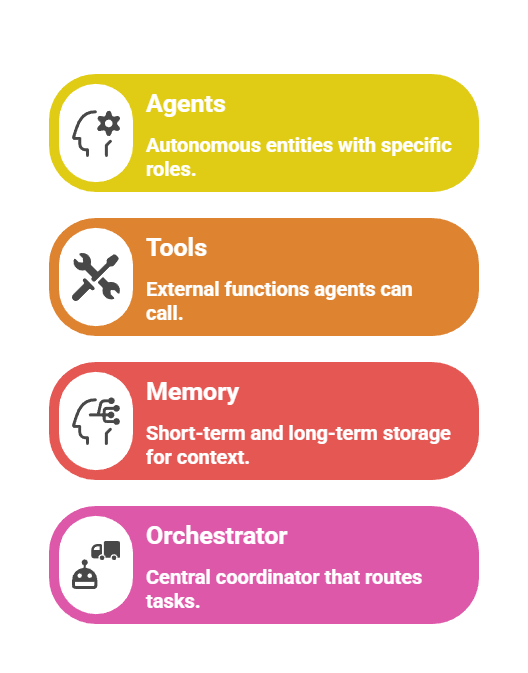
Multi-Agent Systems: Collaborative Intelligence
Multi-agent systems shine in multimodal reasoning by dividing labor, much like a team of experts tackling a project. Instead of a single LLM struggling with overload, agents debate, critique, and refine outputs collaboratively.
Picture a system diagnosing plant disease from a photo and user description: one agent extracts visual features, another cross-references textual symptoms, and a third queries a botanical database. Frameworks like AutoGen or CrewAI implement this via message-passing protocols.
Architectures and Workflow Patterns
Common patterns include hierarchical (supervisor-subordinate) and peer-to-peer structures. Here's a step-by-step workflow for a typical multi-agent setup:
1. Task Decomposition: Orchestrator breaks input into subtasks using chain-of-thought prompting.
2. Agent Assignment: Route to specialists (e.g., text agent for NLP, vision agent for images).
3. Tool Invocation: Agents call tools if needed—e.g., image_analyzer.describe("plant_photo.jpg")
4. Consensus Building: Agents share outputs; a critic agent evaluates for consistency.
5. Iteration or Termination: Loop until confidence threshold met or final answer synthesized.
Code Snippet (Python with LangChain)
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain.tools import Tool
vision_tool = Tool(name="VisionAnalyzer", func=analyze_image, description="Analyzes images for objects and conditions")
planner = create_react_agent(llm=llm, tools=[vision_tool])
# Execute multimodal query
result = planner.invoke({"input": "Describe this plant image and suggest care tips: [image_url]"})This pattern reduces hallucination by 30-50% in benchmarks like GAIA, per recent studies from Microsoft Research (2024).
Integrating Tool Use for Grounded Reasoning
Tool use transforms agents from speculative reasoners into action-oriented systems. In multimodal contexts, tools bridge LLMs' limitations—like outdated knowledge or inability to "see" images—ensuring outputs are verifiable.
Agents decide when to use tools via ReAct (Reason + Act) prompting: "Think step-by-step, then act with a tool if needed." Best practices include tool retrieval (dynamically selecting from 100+ options) and error handling (retry with refined prompts).
Practical Examples in Action
Consider these real-world scenarios:
1. E-commerce Virtual Assistant: Processes product image + query ("Find similar shoes"). Vision agent extracts style/color; search agent queries inventory API.
2. Medical Triage Bot: Analyzes patient photo (rash) + symptoms text. Dermatology agent uses vision tools; reasoning agent cross-checks PubMed via API.
3. Content Creation Suite: Generates video scripts from storyboard images + text brief. Multimodal agent fuses inputs, tools edit timelines via FFmpeg.
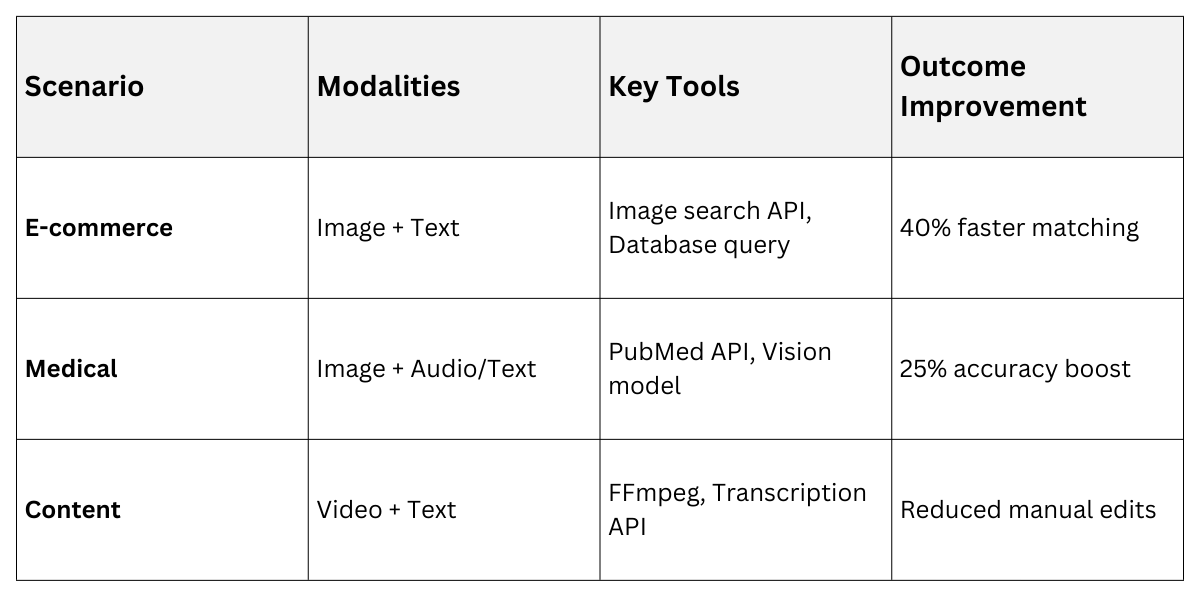
Industry standards like OpenAI's Assistants API (updated 2025) embed these natively, supporting parallel tool calls.
Challenges and Best Practices
While powerful, agentic systems face hurdles like infinite loops, high latency, and cost. Multimodality amplifies this—processing a 4K image takes seconds versus milliseconds for text.
Mitigate With
.png)
Pro Tip: Start simple—prototype with single-agent ReAct before scaling to multi-agent. Test on diverse multimodal datasets like Visual Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks.
