Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) are alignment techniques used to improve the behavior of large language models according to human preferences.
In RLHF, models are first trained using supervised data and then refined using a reward model learned from human feedback.
The model is optimized through reinforcement learning to maximize this reward, encouraging outputs that are helpful, safe, and aligned with human values.
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) simplifies this process by directly optimizing the model using human preference pairs without requiring an explicit reward model or reinforcement learning loop.
DPO is more stable and computationally efficient while achieving similar alignment performance.
Understanding RLHF: The Foundation of Aligned Generative Models
RLHF emerged as a breakthrough in 2022 from OpenAI's InstructGPT work, transforming how we train LLMs to follow instructions effectively. It combines supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement learning, using human preferences to guide model behavior.
Core Components of RLHF
RLHF operates through a three-stage pipeline that refines a pre-trained LLM into an aligned assistant. This process starts with human-annotated data and evolves into a reward model that scores outputs.
-Picsart-CropImage.png)
Here's a simple Python snippet illustrating a conceptual PPO step (using Hugging Face's TRL library for practicality)
from trl import PPOTrainer, PPOConfig
config = PPOConfig(model_name="gpt2", learning_rate=1.41e-5)
ppo_trainer = PPOTrainer(config=config, model=policy_model, ref_model=ref_model)
# Train on preference data
ppo_trainer.step(prompts, responses, rewards)This setup ensures the model generates preferred outputs without collapsing into repetitive or unsafe behaviors.
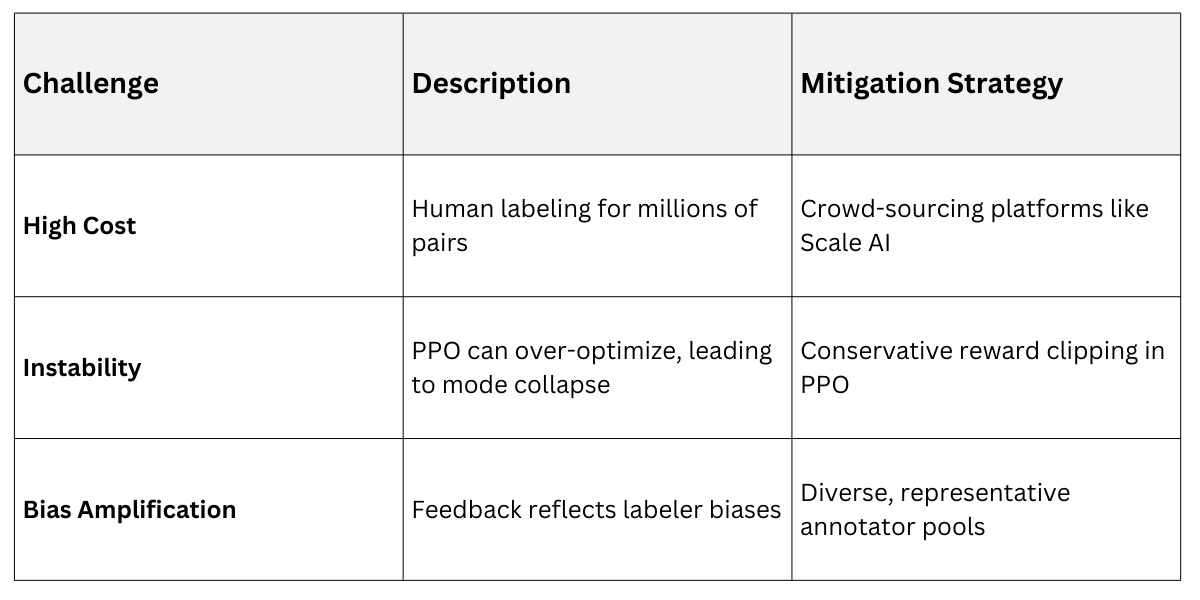
Practical Applications and Challenges
Consider a customer support chatbot: RLHF trains it to prioritize empathetic, accurate responses over generic ones.
In prompt design, RLHF-aligned models better interpret nuanced instructions like "Explain quantum computing like I'm 10, but add technical depth for experts."
However, RLHF faces scalability hurdles—collecting human feedback is expensive, and PPO training is computationally intensive, often requiring clusters of GPUs.
 Direct Preference Optimization (DPO): A Simpler Path to Alignment
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO): A Simpler Path to Alignment
DPO, introduced by Rafael Rafailov et al. in 2023, revolutionizes alignment by bypassing the explicit reward model and RL phase of traditional RLHF.
It directly optimizes the policy using preference data, making it more efficient and stable.
How DPO Works
DPO reframes preference alignment as a binary classification task on the model's own logits. Given a prompt and paired responses (chosen vs. rejected), it maximizes the likelihood of the preferred response relative to the rejected one.
The key insight: Preferences implicitly define an optimal reward function, derived from the base model's probabilities. Training minimizes a loss that encourages the model to favor "winning" responses without needing PPO.
1. Collect Preference Dataset: Pairs like (prompt, good_response, bad_response).
2. Compute Implicit Rewards: Use the reference model to estimate rewards for each response.
3. Optimize Directly: Fine-tune the policy model with DPO loss, typically in 1-2 epochs on consumer hardware.
Example using the Hugging Face trl library
from trl import DPOTrainer, DPOConfig
config = DPOConfig(model_name="meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", beta=0.1)
trainer = DPOTrainer(config=config, model=model, ref_model=ref_model, train_dataset=pref_dataset)
trainer.train()This approach achieves comparable results to RLHF but trains 10x faster.
DPO vs. RLHF
DPO addresses RLHF's pain points, offering a drop-in replacement for many use cases in generative AI pipelines.
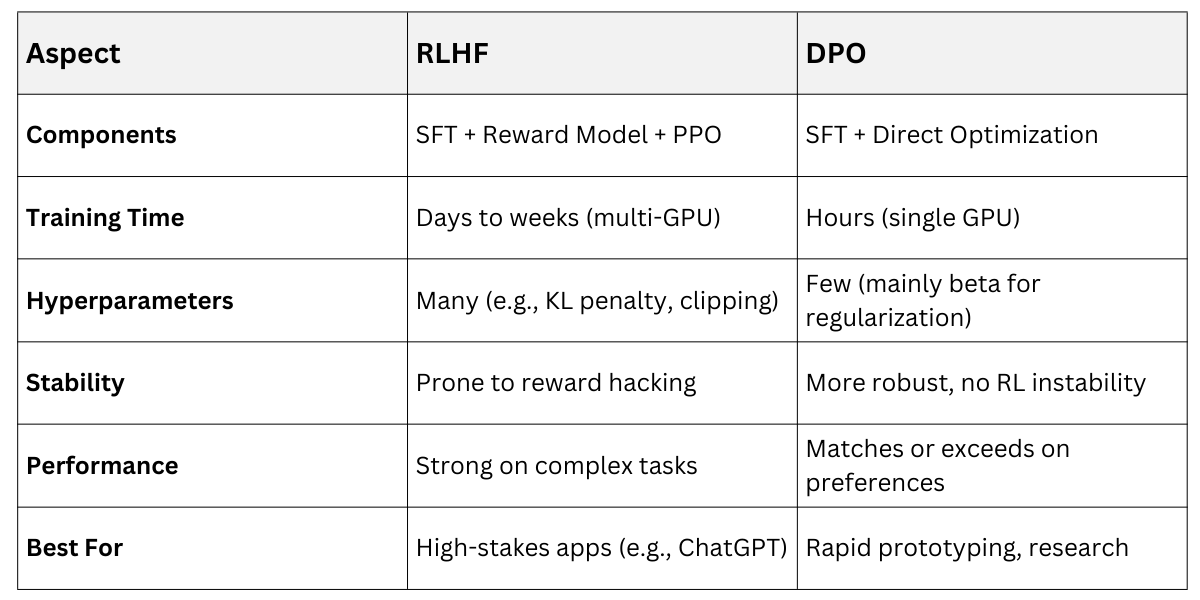
In practice, DPO excels in prompt design workflows—fine-tune a base model on domain-specific preferences (e.g., legal writing: precise and formal) without RL overhead.
Advanced Techniques and Best Practices
Both methods integrate seamlessly with course topics like prompt engineering and architectural scaling.
Iterating with Human Feedback Loops
For ongoing alignment:
.png)
Practical Example: In a healthcare chatbot, rank responses for empathy and accuracy, then apply DPO to specialize prompts like "Summarize patient symptoms without diagnosing."
Industry Standards and Tools
1. Datasets: Anthropic's HH-RLHF, OpenAI's WebGPT comparisons—publicly available on Hugging Face.
2. Frameworks: TRL (Transformer Reinforcement Learning) for both RLHF and DPO; Alignment Handbook for recipes.
Best Practices: Always include a reference model to prevent overfitting; monitor KL divergence to retain base capabilities.
Integrating RLHF and DPO into Generative Architectures
These techniques supercharge prompt design by making models inherently better at following instructions.
1. Prompt Chaining: Aligned models handle multi-step prompts reliably, e.g., "First analyze, then generate code."
2. Scaling Laws: RLHF/DPO gains compound with model size—Llama-3 used RLHF variants for superior instruction-following.
3. Edge Cases: Robust to adversarial prompts, reducing jailbreaks.
In your projects, start with DPO on a 7B model for quick wins, scaling to RLHF for enterprise deployments.
