Self-attention mechanisms and positional encodings are fundamental components of GPT-style transformer models. Self-attention allows each token in a sequence to attend to all other tokens, enabling the model to capture long-range dependencies and contextual relationships efficiently.
Since transformers do not process data sequentially like recurrent models, positional encodings are added to token representations to provide information about the order and position of tokens in the sequence.
Self-Attention Mechanisms
Self-attention is the heart of transformer models, allowing the network to weigh the importance of different words in a sequence relative to each other.
It computes relationships dynamically, making GPT models excel at capturing context over long texts. Let's break it down step by step.
Imagine reading a sentence like "The bank by the river was flooded"—self-attention helps the model decide if "bank" means a financial institution or a riverbank by looking at surrounding words.
Core idea: Every word (or token) attends to every other word in the sequence, computing a relevance score.
Key benefit: Unlike CNNs or RNNs, it processes all tokens in parallel, speeding up training on massive datasets.
Self-attention uses three vectors per token: Query (Q), Key (K), and Value (V), derived from the input embeddings via learned weights.
Here's the Process in Numbered Steps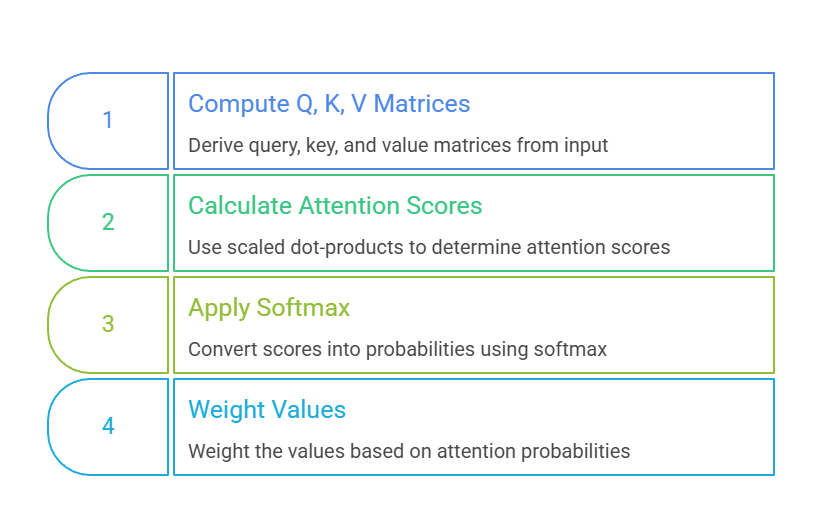
This approach, from the 2017 "Attention is All You Need" paper, remains the industry standard.
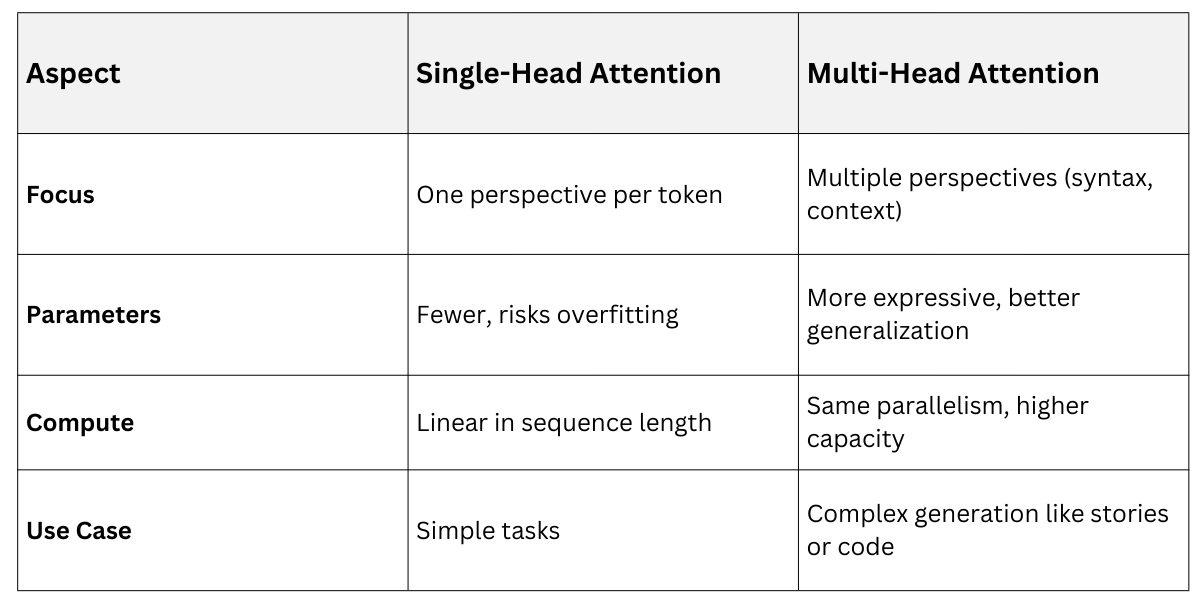
Multi-Head Attention: A single attention head might miss nuances, so GPT uses multi-head attention—multiple attention layers running in parallel.
Each head learns different relationships, like syntax in one and semantics in another. Outputs concatenate and project back.
Single vs. Multi-Head Attention
Code Example (PyTorch)
import torch.nn as nn
multihead_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=512, num_heads=8)In practice, for a Python web app generating user prompts, multi-head attention ensures coherent outputs.
Positional Encodings
Transformers lack built-in sequence awareness since they process tokens in parallel—enter positional encodings, which inject order information.
These fixed or learned vectors add position signals to embeddings, letting the model distinguish "cat chased dog" from "dog chased cat." In GPT-style models, they enable autoregressive generation, predicting the next token based on all priors.
Why Positional Encodings Matter: Without them, the model treats sequences as bags of words, losing order critical for language.
GPT-2 used fixed sinusoidal encodings; newer ones include relative positional methods for better long-context handling (up to 128k tokens).
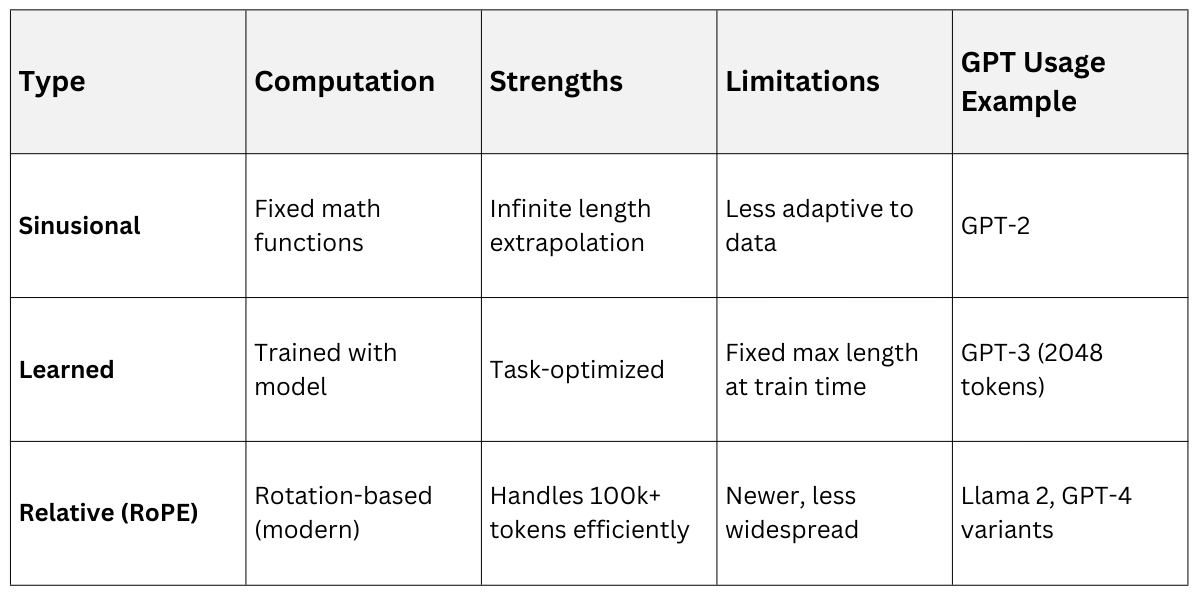
Types of Positional Encodings
Two main approaches dominate:
1. Sinusoidal (Absolute) Positional Encoding: Uses sine and cosine functions based on position and dimension.
Pros: Fixed, no training needed; works for longer sequences.
Cons: Less adaptive to specific data patterns.
2. Learned Positional Embeddings: Trainable vectors added to token embeddings (GPT-3 style).
More flexible for task-specific ordering.
Common in decoder-only models.
Encoding Types
Practical Example: In a data science course generator, positional encodings ensure ordered outputs: "1. Import libraries, 2. Load data..."
Code Snippet (Hugging Face)
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer, GPT2Model
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2')
# Positional encodings added automatically in modelIntegration in GPT-Style Models
GPT models stack self-attention and positional encodings in a decoder-only transformer architecture, optimized for next-token prediction.
Token embeddings plus positional encodings feed into multi-head self-attention layers, followed by feed-forward networks and layer normalization. This repeats 12–175+ times.
Key Flow (Numbered Process)
 - visual selection-Picsart-CropImage.png)
Best Practices
1. Use causal masking in self-attention to prevent future peeking.
2. Scale embeddings appropriately (768 dimensions for base GPT).
3. For long contexts, adopt Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE).
In FastAPI apps, Hugging Face implements this easily.
Fine-tuning Example
from transformers import GPT2LMHeadModel, Trainer
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained('gpt2')
# Add your course dataset hereClass Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
