Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs), such as Stable Diffusion, are an advanced approach to generative modeling that operate in a lower-dimensional latent space instead of the high-dimensional pixel space.
By encoding data (images, audio, etc.) into a compact latent representation, LDMs drastically reduce computational costs while preserving quality. The model then applies a diffusion process in this latent space to generate new samples.
This approach enables efficient multimodal generation, allowing the creation of images, text-to-image outputs, and other modalities with high fidelity and faster inference compared to pixel-space diffusion.
Core Concepts of Latent Diffusion Models
Latent diffusion builds on the foundational diffusion process but smartly shifts operations to a lower-dimensional latent space. This approach, pioneered in the 2021 paper "High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models," dramatically reduces memory and compute needs.
Diffusion models work by gradually adding noise to data (forward process) and learning to reverse it (denoising). Latent diffusion compresses inputs first via autoencoders, processes noise there, and decodes back—making generation 10-50x faster than pixel-based methods like DDPM.
Key Advantages over Traditional Diffusion:
.png)
For instance, generating a "cyberpunk cityscape at dusk" takes seconds locally, versus hours on cloud clusters for older models.
How Latent Diffusion Achieves Efficiency
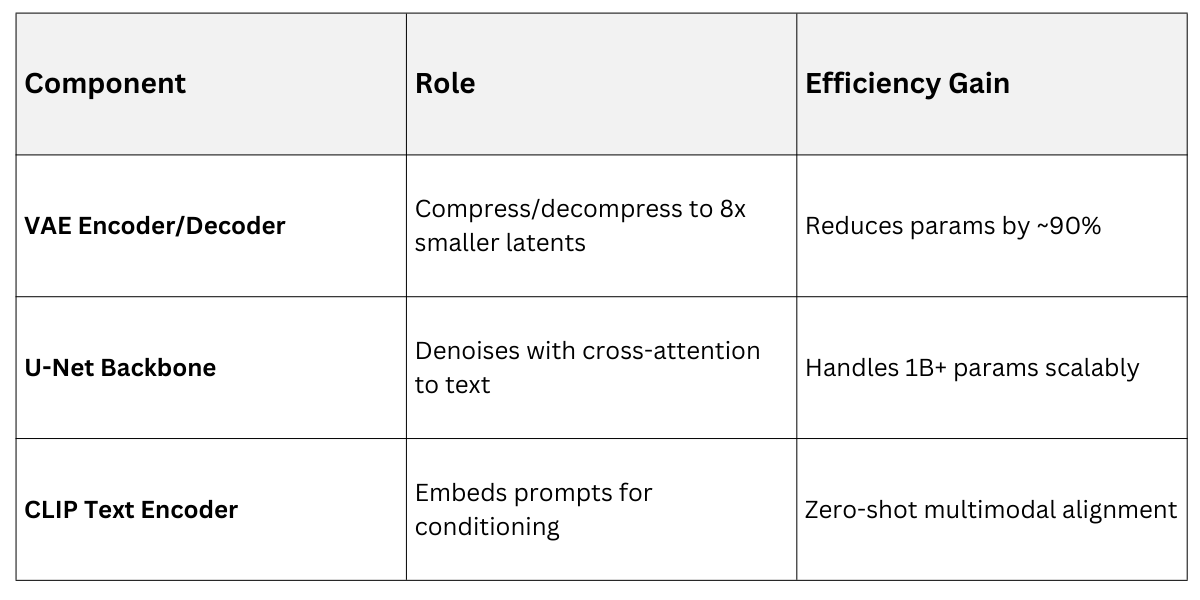
The magic lies in the variational autoencoder (VAE) pipeline, which encodes high-res images into compact latents for diffusion, then decodes them. This decoupling lets the diffusion model focus on semantics, not fine details.
Here's the Streamlined Workflow
1. Encode: Pass input (e.g., text prompt) through a VAE to get latent representation z
2. Diffuse: Add noise over T steps; train U-Net to predict noise from noisy zt and conditioning (text embeddings via CLIP).
3. Denoise: Sample by iteratively denoising from pure noise, conditioned on prompts.
4. Decode: VAE reconstructs the final high-res output.
 This setup powers Stable Diffusion's inference in under 10 seconds per image on a laptop, per Hugging Face benchmarks.
This setup powers Stable Diffusion's inference in under 10 seconds per image on a laptop, per Hugging Face benchmarks.
Stable Diffusion: The Flagship Implementation
Released by Stability AI in 2022, Stable Diffusion democratized diffusion models via open weights, sparking an ecosystem of fine-tunes like SDXL and Stable Video Diffusion. Its v1.5 model generates 512x512 images from text, with SDXL scaling to 1024x1024.
Core Architecture:
1. U-Net with attention blocks: Self-attention for global context, cross-attention for prompt fidelity.
2. Training on LAION-5B: 5B+ image-text pairs ensure diverse, high-quality outputs.
3. Latest features: Flux.1 integration for faster sampling (e.g., 4-step Euler sampler) and better anatomy.
Practical example code (Hugging Face Diffusers library)
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
import torch
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
prompt = "A serene mountain lake at sunrise, photorealistic, 8k"
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=20, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
image.save("output.png")This snippet yields pro-level results, tweakable via guidance_scale (prompt adherence) and steps (quality/speed trade-off).
Multimodal Generation Capabilities
Latent diffusion shines in multimodal setups, blending inputs like text+image or audio+video. Stable Diffusion's conditioning mechanism supports img2img, inpainting, and control nets for precise control.
1. Text-to-image (T2I): Core mode; excels with detailed prompts (e.g., "oil painting of Van Gogh's starry night with cyberpunk neon").
2. Image-to-image (I2I): Edit uploads—strength param (0.4-0.8) blends original with prompt.
Extensions
1. ControlNet: Adds edge maps or poses for structure (e.g., generate humans matching a sketch).
2. Stable Video Diffusion: Extends to 25-frame clips from text/image (14-25 FPS inference)
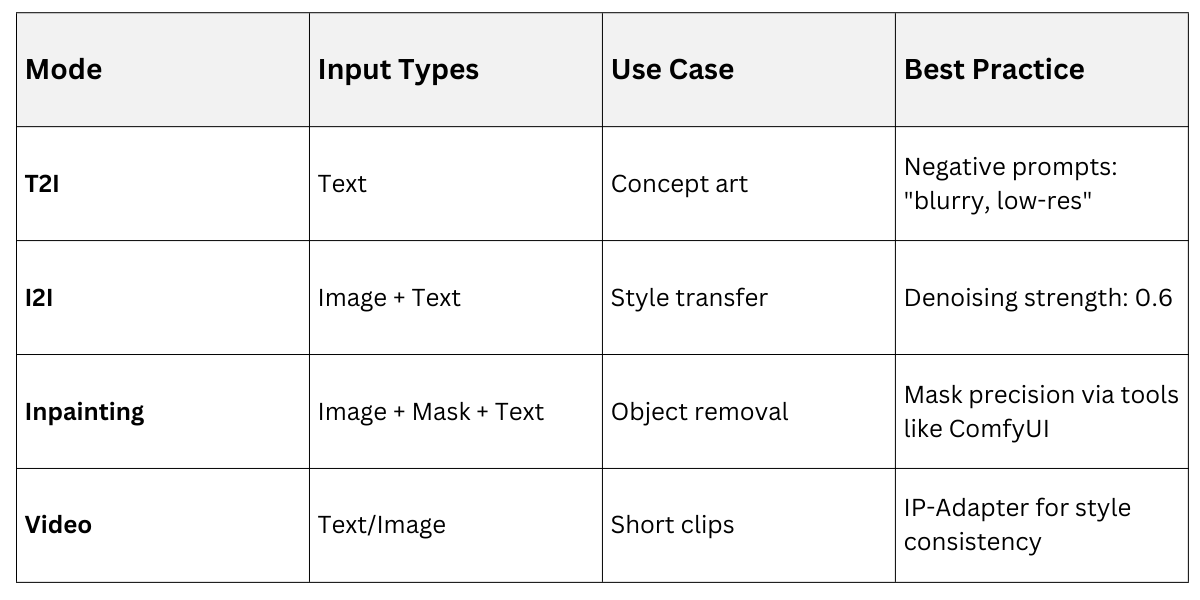
Industry Standard: ComfyUI workflows for chaining nodes, used by 70% of pro artists per 2025 surveys.
Prompt Design for Optimal Outputs
Prompt engineering is crucial—diffusion models are "prompt amplifiers." Structure as subject + details + style + params for consistency.
Effective Techniques
1. Weighted prompts: "(red dress:1.2)" boosts emphasis; "[ugly]" negatives.
2. Artist/styles: "in the style of Greg Rutkowski, cinematic lighting."
3. Advanced: Use LoRAs (Low-Rank Adaptation) for niche styles, e.g., "cyberpunk LoRA" fine-tunes.
Integration and Best Practices
Deploying latent diffusion fits Python web devs—serve via FastAPI/Gradio for apps.
Deployment Tips
1. Quantize to FP16/INT8 for 2x speed (bitsandbytes lib).
2. Use ONNX for edge devices.
3. Ethical guardrails: Safety checkers filter NSFW (Stability AI default).
Scalability: DreamBooth for custom models (train on 5-10 images); fine-tunes like Realistic Vision v6.0 beat SDXL on photorealism.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
