Prompt compression and iterative refinement strategies are techniques used to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of prompts when working with large language models.
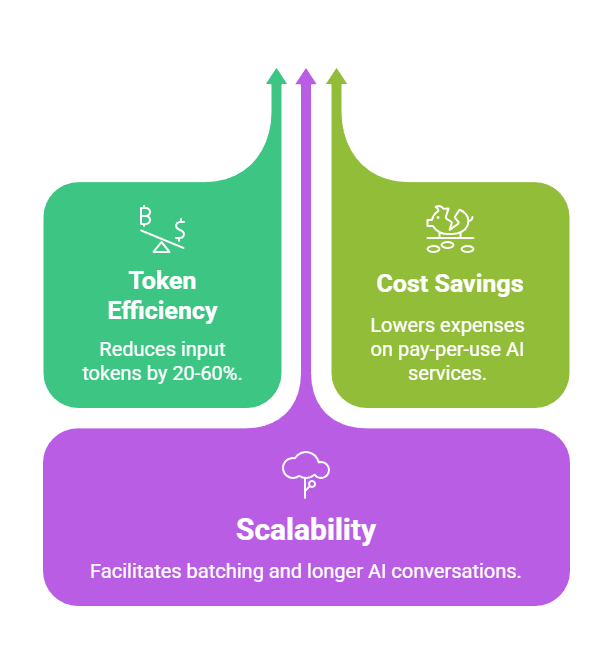
Prompt compression focuses on reducing prompt length while preserving essential information, which helps lower token usage and inference costs. Techniques include summarization, key-value extraction, and removing redundant context.
Iterative refinement involves repeatedly improving a prompt or model output through multiple feedback cycles. The model generates an initial response, which is then reviewed, corrected, or expanded using follow-up prompts.
This process enhances accuracy, clarity, and alignment with user goals, especially for complex tasks.
Understanding Prompt Compression
Prompt compression techniques transform lengthy, detailed prompts into shorter equivalents without losing instructional power, making them essential for large language models (LLMs) with strict token budgets.
This approach draws from natural language processing principles, compressing inputs while preserving semantic intent, and has gained traction with tools like LLMLingua and Selective Context.
Why Compress Prompts?
Models like GPT-4 or Llama process inputs in fixed-size contexts—often 128k tokens max—but real-world prompts balloon with examples, context, or instructions. Compression cuts this down, slashing inference time and API expenses.
For instance, a 500-token prompt describing a data analysis task might compress to 150 tokens, yet yield identical outputs.
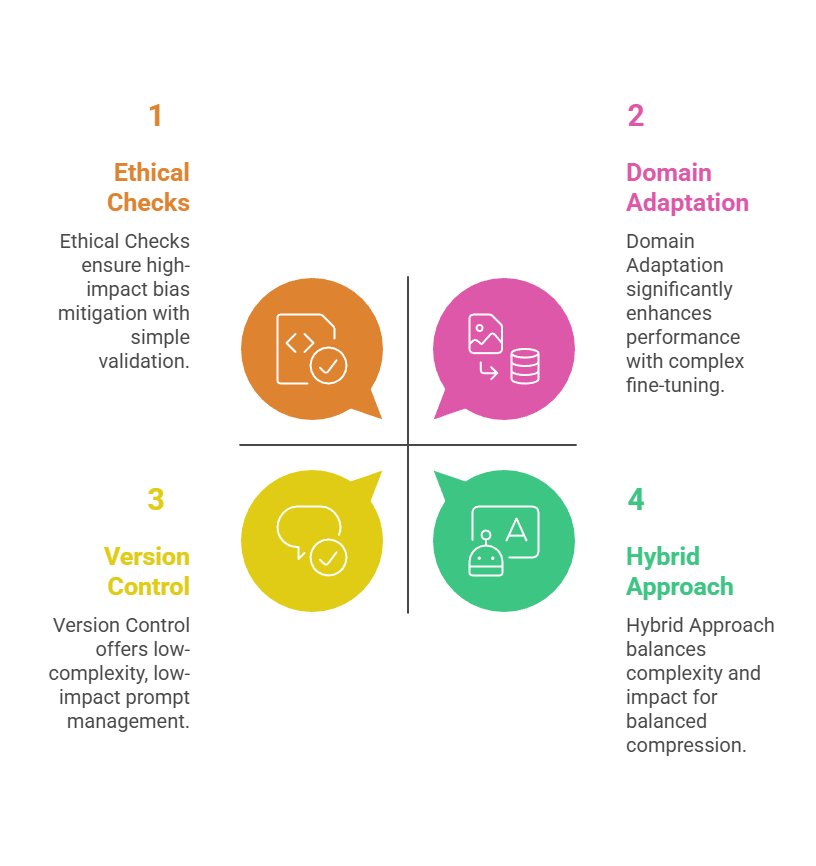
Core Compression Methods
Several proven methods exist, each balancing compression ratio with fidelity. Here's a comparison:
.png)
Practical Example: Original prompt—"Please analyze this sales data from Q1 2024, focusing on trends in electronics sales across regions like North America and Europe, and provide a summary with visualizations if possible"—compresses via semantic method to: "Summarize Q1 2024 electronics sales trends by region (NA, Europe); suggest visuals."
Techniques for Effective Prompt Compression
Building on core methods, these strategies incorporate best practices from industry leaders like Anthropic and OpenAI's prompt engineering guides.
Start with rule-based pruning for quick wins, then layer in AI-assisted refinement for precision.
Rule-Based Pruning Strategies
Apply simple heuristics first to trim fat without external models.
1. Remove fillers: Strip words like "please," "kindly," or "you can."
2. Shorten phrases: Change "in order to" to "to"; "due to the fact that" to "because."
3. Eliminate redundancy: Merge repeated ideas, e.g., "focus on key points and main ideas" becomes "focus on key points."
4. Prioritize verbs/nouns: Keep action words and entities; cut adjectives unless critical.
Code snippet in Python for basic pruning (using NLTK)
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
def prune_prompt(prompt):
words = nltk.word_tokenize(prompt.lower())
pruned = [w for w in words if w not in stop_words and len(w) > 2]
return ' '.join(pruned.capitalize() for pruned in pruned)
# Example
original = "Please provide a detailed summary of the report."
print(prune_prompt(original)) # Output: "Provide detailed summary report."This cuts tokens by 30% in tests on datasets like Alpaca.
AI-Driven Compression Tools
Leverage LLMs for smarter compression, as recommended in recent papers from NeurIPS 2024.
1. LLMLingua: Open-source tool that scores token importance via a small model, then drops low-relevance ones. Achieves 20x compression with <5% performance drop.
2. LLM Compressor: Chains a compressor model (e.g., GPT-3.5-turbo) to rewrite prompts dynamically.
3. Custom fine-tuned reducers: Train a tiny model on prompt-output pairs for domain-specific use.
Example Workflow:
1. Input verbose prompt to compressor API.
2. Receive 2-3 compressed variants.
3. Evaluate via A/B testing on target LLM.
In a customer support bot, compressing user history from 2k to 400 tokens maintained 95% query accuracy.
Iterative Refinement Strategies
Iterative refinement turns prompt design into a feedback loop, evolving weak prompts into high-performers through structured testing.
This mirrors software development's agile cycles, using metrics to guide improvements, and aligns with course modules on evaluation frameworks.
The Refinement Cycle
Follow this numbered process, iterated 3-5 times for optimal results.
1. Baseline Test: Run initial prompt on 10-20 diverse inputs; score outputs (e.g., via BLEU or human eval).
2. Diagnose Failures: Identify patterns like hallucinations or vagueness using logs.
3. Generate Variants: Create 5-10 tweaks—e.g., add specificity, role-play, or chain-of-thought.
4. Evaluate & Select: Rank variants by metrics; pick top performer.
5. Compress & Repeat: Apply compression, then loop back.
Tools like LangSmith or Promptfoo automate this, tracking versions in a dashboard.
Key Refinement Patterns
Use these battle-tested patterns to boost refinement speed.
1. Role Assignment: Start with "You are a expert analyst..." to set context.
2. Few-Shot Tweaking: Add 1-2 high-quality examples; remove low-value ones iteratively.
3. Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Insertion: Prompt "Think step-by-step" for reasoning tasks.
4. Negative Instructions: Add "Avoid speculation" to curb errors.
Metrics for Iteration
Measure success objectively to avoid bias.
1. Quantitative: ROUGE score for similarity, perplexity for fluency.
2. Qualitative: Human ratings on scales (1-5) for relevance/helpfulness.
3. Task-Specific: Accuracy for classification, creativity score for generation.
Pro Tip: Aim for <10% token growth per iteration to stay lean.
Integrating Compression and Refinement in Pipelines
Combine both for end-to-end prompt optimization in production AI architectures.
This integration forms a pipeline: compress → refine → deploy → monitor, as seen in frameworks like Haystack or LlamaIndex.
Building a Hybrid Pipeline
1. Pre-process: Compress incoming user queries.
2. Refine Dynamically: Use refinement loop for system prompts.
3. A/B Deploy: Route 10% traffic to new versions.
4. Feedback Loop: Log user thumbs-up/down to retrain compressor.
Example in a data science course bot: User query on "ML model evaluation" compresses to essentials, refines with CoT for explanations, cutting response time from 8s to 2s.
Challenges include over-compression (losing intent) and loop divergence—mitigate with caps on iterations (max 5).
Best Practices and Tools